Questões de Concurso
Sobre interpretação de texto | reading comprehension em inglês
Foram encontradas 9.475 questões
TEXT 1
What is administrative excellence?
Administrative Professionals perform some of the toughest functions in an office. Not only are you required to keep pace with ever-changing technology, you need to work with and through many people to meet deadlines, resolve conflicts, gather information, and coordinate schedules and logistics. Additionally, you are often the first point-of-contact for customers – your competence and professionalism in meeting their demands might be one of the most important factors in how your organization is perceived in the marketplace. To satisfy the needs of so many, your technical skills and your interpersonal skills must be well-balanced to generate efficient and effective results.
Administrative excellence pertains to the quality of work and the caliber of service that you provide in carrying out your responsibilities. Excellence by definition exceeds the routine expectations of managers, coworkers, and other customers, but it is a standard first set by you. It is something that many aspire to and work hard to deliver. I once read that excellence means "you are better today than you were yesterday, but not as good as you will be tomorrow." With that understanding, you can see there is no finish line. Excellence is a commitment to continually do and give your best.
Although we each have personal standards and differing values in terms of excellence, there are a few things that help to streamline administrative efforts in reaching high levels of job performance. Here are what I considered to be the "5Ps" of administrative excellence:
1. Perception – Self-awareness of behaviors and skills that maximize strengths and minimize weaknesses.
Know yourself and what you like and what you dislike about your job. Pay attention to those activities that excite and engage you. Typically, these are things that come naturally or easily for you – your strengths. Find opportunities to do more of what you love to do – you’ll be happier and more satisfied with your work. Take control and find solutions for those parts of your job that are less fulfilling so that your emotions and attitude don’t work against you.
2. Purpose – Understanding the importance of job responsibilities and identifying with the overall objectives of the team, department, and organization.
It’s one thing to know how to do your job, but it’s more important to know why you do what you do. Understanding your role in the bigger picture of organizational success helps to ignite feelings of inclusion and professional pride.
3. Progress – Ability to think progressively for continuous personal and professional improvement.
Challenge yourself to try new things and new ways of doing routine things. Don’t let yourself stagnate or become too comfortable – seize opportunities to showcase your skills or push self-imposed limitations. People rarely gain a professional edge when others can’t see or don’t know what they are capable of achieving.
4. Partnership – Willingness and ability to foster good relationships and teamwork with coworkers, managers, and customers.
Good relationships are the foundation for resourcefulness in your job. Treat others with respect. Do what you say you will do, offer to help others, exhibit a sense of urgency in responding to requests, and extend common courtesy – when others reciprocate, a trusting partnership is formed.
5. Professionalism – High standards of appearance, personal conduct, work product, and expertise.
Don’t leave doubts in the minds of others. Match image with skills and knowledge to help shape the thoughts and experiences of others. Continue to learn and produce accurate, timely work and your reputation and credibility will "speak for itself."
There are many other measurements of excellence. Find things that are unique about you and make your pathway to excellence your own. No one else will do it or achieve it in exactly the same manner. It’s often the small things that make a person stand out in a big way. Several years ago, a manager described his admin’s stellar performance in this way, "I don’t know how else to explain it…everything she does for me comes back just a little bit better than I expected it to." That’s a strong endorsement for administrative excellence – a little effort, a lot of admiration.
©Administrative Excellence – 2010 (Adapted from: https://adminexcellence.wordpress.com/2010/03/16/what-is-administrative-excellence/, in 12/01/2017)
TEXT 1
What is administrative excellence?
Administrative Professionals perform some of the toughest functions in an office. Not only are you required to keep pace with ever-changing technology, you need to work with and through many people to meet deadlines, resolve conflicts, gather information, and coordinate schedules and logistics. Additionally, you are often the first point-of-contact for customers – your competence and professionalism in meeting their demands might be one of the most important factors in how your organization is perceived in the marketplace. To satisfy the needs of so many, your technical skills and your interpersonal skills must be well-balanced to generate efficient and effective results.
Administrative excellence pertains to the quality of work and the caliber of service that you provide in carrying out your responsibilities. Excellence by definition exceeds the routine expectations of managers, coworkers, and other customers, but it is a standard first set by you. It is something that many aspire to and work hard to deliver. I once read that excellence means "you are better today than you were yesterday, but not as good as you will be tomorrow." With that understanding, you can see there is no finish line. Excellence is a commitment to continually do and give your best.
Although we each have personal standards and differing values in terms of excellence, there are a few things that help to streamline administrative efforts in reaching high levels of job performance. Here are what I considered to be the "5Ps" of administrative excellence:
1. Perception – Self-awareness of behaviors and skills that maximize strengths and minimize weaknesses.
Know yourself and what you like and what you dislike about your job. Pay attention to those activities that excite and engage you. Typically, these are things that come naturally or easily for you – your strengths. Find opportunities to do more of what you love to do – you’ll be happier and more satisfied with your work. Take control and find solutions for those parts of your job that are less fulfilling so that your emotions and attitude don’t work against you.
2. Purpose – Understanding the importance of job responsibilities and identifying with the overall objectives of the team, department, and organization.
It’s one thing to know how to do your job, but it’s more important to know why you do what you do. Understanding your role in the bigger picture of organizational success helps to ignite feelings of inclusion and professional pride.
3. Progress – Ability to think progressively for continuous personal and professional improvement.
Challenge yourself to try new things and new ways of doing routine things. Don’t let yourself stagnate or become too comfortable – seize opportunities to showcase your skills or push self-imposed limitations. People rarely gain a professional edge when others can’t see or don’t know what they are capable of achieving.
4. Partnership – Willingness and ability to foster good relationships and teamwork with coworkers, managers, and customers.
Good relationships are the foundation for resourcefulness in your job. Treat others with respect. Do what you say you will do, offer to help others, exhibit a sense of urgency in responding to requests, and extend common courtesy – when others reciprocate, a trusting partnership is formed.
5. Professionalism – High standards of appearance, personal conduct, work product, and expertise.
Don’t leave doubts in the minds of others. Match image with skills and knowledge to help shape the thoughts and experiences of others. Continue to learn and produce accurate, timely work and your reputation and credibility will "speak for itself."
There are many other measurements of excellence. Find things that are unique about you and make your pathway to excellence your own. No one else will do it or achieve it in exactly the same manner. It’s often the small things that make a person stand out in a big way. Several years ago, a manager described his admin’s stellar performance in this way, "I don’t know how else to explain it…everything she does for me comes back just a little bit better than I expected it to." That’s a strong endorsement for administrative excellence – a little effort, a lot of admiration.
©Administrative Excellence – 2010 (Adapted from: https://adminexcellence.wordpress.com/2010/03/16/what-is-administrative-excellence/, in 12/01/2017)
Judge the following item according to text 19A3AAA.
Students learn errors from other students.
Judge the following item according to text 19A3AAA.
Overextension is one type of overgeneralization error.
Judge the following item according to text 19A3AAA.
The text defends that the more different a grammar structure
in the second language is, the longer a learner will take to
acquire it.
Judge the following item according to text 19A3AAA.
First language learners’ errors are similar to second language
learners’ errors despite the latter’s first language.
Based on the text 19A1BBB, judge the following item.
It can be concluded from the text that current times call for
action, change and diversity in language teaching.
Judge the following item, concerning the ideas and linguistic aspects of text 19A1AAA.
Palmer must have had another job prior to working as a teacher
of EFL.
Read the following text.
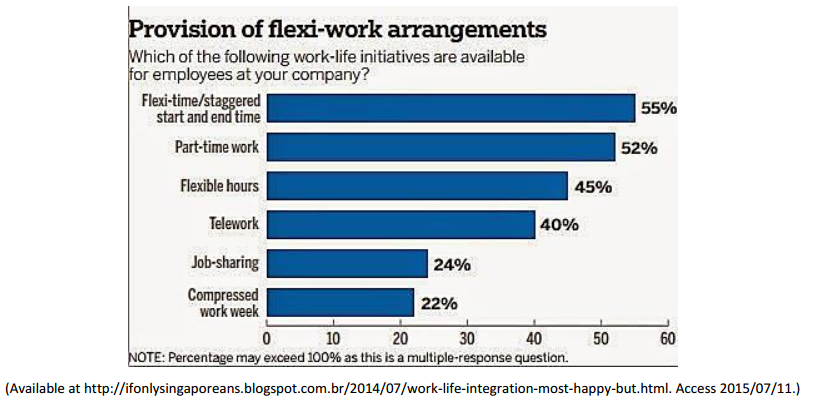
In work-life interaction, it is clear from the chart that
Based on the text, judge the following items.
The nutritional content of these fad diets is so complex
because they are based on a scientific theory.
Based on the text, judge the following items.
In paragraph 1, according to some doctors, fad diets have
recently contributed to making the obesity issue much
worse.
Based on the text, judge the following items.
It is clearly stated in the text that there are now more
cats than dogs in British homes.
Based on the text, judge the following items.
In 1993 the dog population in Britain increased
by 7 million.
Based on the text, judge the following items.
“The dog” (line 1) means a specific type of animal. Not a
specific dog.
 these questions 50 years ago, or in
another 50 years, we might see dramatically different results. Women are pursuing careers on par with men, yet women are still a little
more responsible for things at home.”
these questions 50 years ago, or in
another 50 years, we might see dramatically different results. Women are pursuing careers on par with men, yet women are still a little
more responsible for things at home.”




