Questões de Concurso
Comentadas para analista de recursos humanos
Foram encontradas 1.681 questões
Resolva questões gratuitamente!
Junte-se a mais de 4 milhões de concurseiros!
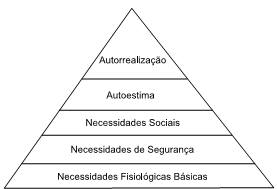
Assinale a alternativa que contém uma necessidade de autorrealização.
Pode-se afirmar que está-se diante de uma liderança
Das alternativas a seguir, assinale a que apresenta características desse modelo.
No Brasil, o Ministério da Saúde contabilizou 337 casos no dia 11 de outubro, número que saltou para 824 em duas semanas, distribuídos principalmente entre Oiapoque, no Amapá, Feira de Santana e Riachão do Jacuípe, na Bahia.
A disseminação rápida é atribuída à ausência de imunidade na população e à distribuição dos mosquitos-vetores capazes de transmitir o vírus: Aedes aegypti e Aedes albopictus, os mesmos da dengue.
O nome chicungunha veio da língua Kimakonde, com o significado de “homem que anda arqueado", referência às dores articulares da enfermidade.
Como a história da dengue e da febre amarela, a do chicungunha é indissociável do comportamento humano. O aquecimento e a seca que assolaram o norte da África há 5000 anos forçaram espécies ancestrais dos mosquitos a adaptar-se____________ ambientes __________ os homens armazenavam água.
A febre chicungunha, que emergiu na África, chegou _________Ásia e ___________ Américas.
O chicungunha já é uma ameaça para nós, como demonstra a velocidade de disseminação na Bahia e no Amapá.
(Folha de S.Paulo, 15 nov. 2014. Adaptado)
No Brasil, o Ministério da Saúde contabilizou 337 casos no dia 11 de outubro, número que saltou para 824 em duas semanas, distribuídos principalmente entre Oiapoque, no Amapá, Feira de Santana e Riachão do Jacuípe, na Bahia.
A disseminação rápida é atribuída à ausência de imunidade na população e à distribuição dos mosquitos-vetores capazes de transmitir o vírus: Aedes aegypti e Aedes albopictus, os mesmos da dengue.
O nome chicungunha veio da língua Kimakonde, com o significado de “homem que anda arqueado", referência às dores articulares da enfermidade.
Como a história da dengue e da febre amarela, a do chicungunha é indissociável do comportamento humano. O aquecimento e a seca que assolaram o norte da África há 5000 anos forçaram espécies ancestrais dos mosquitos a adaptar-se____________ ambientes __________ os homens armazenavam água.
A febre chicungunha, que emergiu na África, chegou _________Ásia e ___________ Américas.
O chicungunha já é uma ameaça para nós, como demonstra a velocidade de disseminação na Bahia e no Amapá.
(Folha de S.Paulo, 15 nov. 2014. Adaptado)
Como a história da dengue e da febre amarela, a do chicungunha é indissociável do comportamento humano. (5o parágrafo)
O chicungunha já é uma ameaça para nós, como demonstra a velocidade de disseminação na Bahia e no Amapá. (7o parágrafo)
As expressões em destaque estabelecem, correta e respectivamente, relação de
Leia a charge.

(agazetadoacre.com/noticias/charge-04-02-2015. Acessado em 15.04.2015)
É correto afirmar que o efeito de humor se deve à
The Naval Nuclear Propulsion Program (NNPP) started in 1948. Since that time, the NNPP has provided safe and effective propulsion systems to power submarines, surface combatants, and aircraft carriers. Today, nuclear propulsion enables virtually undetectable US Navy submarines, including the sea-based leg of the strategic triad, and provides essentially inexhaustible propulsion power independent of forward logistical support to both our submarines and aircraft carriers. Over forty percent of the Navy's major combatant ships are nuclear-powered, and because of their demonstrated safety and reliability, these ships have access to seaports throughout the world. The NNPP has consistently sought the best way to affordably meet Navy requirements by evaluating, developing, and delivering a variety of reactor types, fuel systems, and structural materials. The Program has investigated many different fuel systems and reactor design features, and has designed, built, and operated over thirty different reactor designs in over twenty plant types to employ the most promising of these developments in practical applications. Improvements in naval reactor design have allowed increased power and energy to keep pace with the operational requirements of the modern nuclear fleet, while maintaining a conservative design approach that ensures reliability and safety to the crew, the public, and the environment. As just one example of the progress that has been made, the earliest reactor core designs in the NAUTILUS required refueling after about two years while modern reactor cores can last the life of a submarine, or over thirty years without refueling. These improvements have been the result of prudent, conservative engineering, backed by analysis, testing, and prototyping. The NNPP was also a pioneer in developing basic technologies and transferring technology to the civilian nuclear electric power industry. For example, the Program demonstrated the feasibility of commercial nuclear power generation in this country by designing, constructing and operating the Shipping port Atomic Power Station in Pennsylvania and showing the feasibility of a thorium-based breeder reactor.
In: Report on Low Enriched Uranium for Naval Reactor Cores. Page 1. Report to Congress, January 2014. Office of Naval Reactors. US Dept. of Energy. DC 2058 http://fissilematerials.org/library/doe14.pdf
“The Naval Nuclear Propulsion Program (NNPP) started in 1948. Since that time, the NNPP has provided safe and effective propulsion systems to power submarines, surface combatants, and aircraft carriers. Today, nuclear propulsion enables virtually undetectable US Navy submarines, including the sea-based leg of the strategic triad, and provides essentially inexhaustible propulsion power independent of forward logistical support to both our submarines and aircraft carriers.”
Choose the alternative in which the words can properly substitute the ones in bold and underlined, respectively.
The Naval Nuclear Propulsion Program (NNPP) started in 1948. Since that time, the NNPP has provided safe and effective propulsion systems to power submarines, surface combatants, and aircraft carriers. Today, nuclear propulsion enables virtually undetectable US Navy submarines, including the sea-based leg of the strategic triad, and provides essentially inexhaustible propulsion power independent of forward logistical support to both our submarines and aircraft carriers. Over forty percent of the Navy's major combatant ships are nuclear-powered, and because of their demonstrated safety and reliability, these ships have access to seaports throughout the world. The NNPP has consistently sought the best way to affordably meet Navy requirements by evaluating, developing, and delivering a variety of reactor types, fuel systems, and structural materials. The Program has investigated many different fuel systems and reactor design features, and has designed, built, and operated over thirty different reactor designs in over twenty plant types to employ the most promising of these developments in practical applications. Improvements in naval reactor design have allowed increased power and energy to keep pace with the operational requirements of the modern nuclear fleet, while maintaining a conservative design approach that ensures reliability and safety to the crew, the public, and the environment. As just one example of the progress that has been made, the earliest reactor core designs in the NAUTILUS required refueling after about two years while modern reactor cores can last the life of a submarine, or over thirty years without refueling. These improvements have been the result of prudent, conservative engineering, backed by analysis, testing, and prototyping. The NNPP was also a pioneer in developing basic technologies and transferring technology to the civilian nuclear electric power industry. For example, the Program demonstrated the feasibility of commercial nuclear power generation in this country by designing, constructing and operating the Shipping port Atomic Power Station in Pennsylvania and showing the feasibility of a thorium-based breeder reactor.
In: Report on Low Enriched Uranium for Naval Reactor Cores. Page 1. Report to Congress, January 2014. Office of Naval Reactors. US Dept. of Energy. DC 2058 http://fissilematerials.org/library/doe14.pdf
I. investigates more efficient fuels and reactors for the Navy.
II. is concerned about how to spend the financial resources received.
III. has also contributed with the civilian power industry.
The correct assertion(s) is(are)
The Naval Nuclear Propulsion Program (NNPP) started in 1948. Since that time, the NNPP has provided safe and effective propulsion systems to power submarines, surface combatants, and aircraft carriers. Today, nuclear propulsion enables virtually undetectable US Navy submarines, including the sea-based leg of the strategic triad, and provides essentially inexhaustible propulsion power independent of forward logistical support to both our submarines and aircraft carriers. Over forty percent of the Navy's major combatant ships are nuclear-powered, and because of their demonstrated safety and reliability, these ships have access to seaports throughout the world. The NNPP has consistently sought the best way to affordably meet Navy requirements by evaluating, developing, and delivering a variety of reactor types, fuel systems, and structural materials. The Program has investigated many different fuel systems and reactor design features, and has designed, built, and operated over thirty different reactor designs in over twenty plant types to employ the most promising of these developments in practical applications. Improvements in naval reactor design have allowed increased power and energy to keep pace with the operational requirements of the modern nuclear fleet, while maintaining a conservative design approach that ensures reliability and safety to the crew, the public, and the environment. As just one example of the progress that has been made, the earliest reactor core designs in the NAUTILUS required refueling after about two years while modern reactor cores can last the life of a submarine, or over thirty years without refueling. These improvements have been the result of prudent, conservative engineering, backed by analysis, testing, and prototyping. The NNPP was also a pioneer in developing basic technologies and transferring technology to the civilian nuclear electric power industry. For example, the Program demonstrated the feasibility of commercial nuclear power generation in this country by designing, constructing and operating the Shipping port Atomic Power Station in Pennsylvania and showing the feasibility of a thorium-based breeder reactor.
In: Report on Low Enriched Uranium for Naval Reactor Cores. Page 1. Report to Congress, January 2014. Office of Naval Reactors. US Dept. of Energy. DC 2058 http://fissilematerials.org/library/doe14.pdf
“The NNPP has consistently sought the best way to affordably meet Navy requirements by evaluating, developing, and delivering a variety of reactor types, fuel systems, and structural materials.”