Questões de Concurso
Foram encontradas 71.210 questões
Resolva questões gratuitamente!
Junte-se a mais de 4 milhões de concurseiros!
Os Modelos Teóricos de Piaget e Vygotsky seguem condutas Interacionistas, onde o processo do conhecimento é dinâmico e privilegia a interação entre o sujeito que busca conhecer o objeto e o próprio objeto a ser conhecido, estabelecendo-se entre ambos relações recíprocas que modificam tanto o primeiro quanto o segundo. De acordo com o Interacionismo de Vygotsky, assinale a alternativa CORRETA:
I. Vygotsky baseou-se nos conceitos de Marx e Engels para entender o conceito de mediação na interação homem-ambiente pelo uso de instrumentos e signos.
II. Os sistemas de signos: a linguagem, a escrita, o sistema de números, assim como o sistema de instrumentos, são criados pela sociedade no decorrer de sua história e mudam a forma social e o nível do seu desenvolvimento cultural.
III. Para a Teoria Interacionista sócio – histórica, a construção do conhecimento é também realizada através da atividade (como para Piaget), entendida, no entanto, como fator cultural.
IV. Vygotsky apresenta duas ideias principais sobre construção do conhecimento formal na escola. Uma a que se refere como pré-história da aprendizagem e outra como a da área de desenvolvimento potencial ou zona de desenvolvimento proximal.
Com relação ao processo ensino aprendizagem, podemos afirmar que caracterizam a avaliação:
I. A avaliação escolar como um componente do processo de ensino que visa, através da verificação e qualificação dos resultados obtidos, determinar a correspondência destes com os objetivos propostos e, com isso, orientar a tomada de decisões em relação às atividades didáticas.
II. A avaliação escolar cumpre pelo menos três funções: pedagógico-didática, de diagnóstico e de controle.
III. Ajuda a desenvolver capacidades e habilidades, sem refletir a unidade objetivos-conteúdos - possibilitando a revisão do plano de ensino.
IV. A avaliação diagnóstica ocorre no início, durante e no final do desenvolvimento das aulas ou unidades didáticas.
O professor, na concepção _____________________, assume papel de planejar e realizar estratégias no processo ensino aprendizagem, sendo responsável por mantê-lo sobre um rigoroso controle.
Considerando a Didática como Teoria da Instrução e do Ensino, analise as assertivas abaixo, marcando V para Verdadeiro e F para Falso e, em seguida, assinale a alternativa CORRETA:
( ) Tanto a Instrução como o Ensino se modificam em decorrência da sua necessária ligação com o desenvolvimento da sociedade e com as condições reais em que ocorre o trabalho docente.
( ) A Instrução não se refere ao processo e ao resultado de assimilação sólida de conhecimentos sistematizados.
( ) O Currículo não expressa os conteúdos da Instrução.
Read the following text to answer the question.
By Leo Selivan
In this article, informed by the Lexical Approach, I reflect on grammar instruction in the classroom […]. I consider the problems with ‘traditional’ grammar teaching before arguing that what we actually need is more grammar input as well as showing how lexis can provide necessary ‘crutches’ for the learner.
Lexis = vocabulary + grammar
The shift in ELT from grammar to lexis mirrors a similar change in the attitude of linguists. In the past linguists were preoccupied with the grammar of language; however the advances in corpus linguistics have pushed lexis to the forefront. The term ‘lexis’, which was traditionally used by linguists, is a common word these days and frequently used even in textbooks.
Why use a technical term borrowed from the realm of linguistics instead of the word ‘vocabulary’? Quite simply because vocabulary is typically seen as individual words (often presented in lists) whereas lexis is a somewhat wider concept and consists of collocations, chunks and formulaic expressions. It also includes certain patterns that were traditionally associated with the grammar of a language, e.g. If I were you…, I haven’t seen you for ages etc.
Recognising certain grammar structures as lexical
items means that they can be introduced much earlier,
without structural analysis or elaboration. Indeed, since the
concept of notions and functions made its way into language
teaching, particularly as Communicative Language Teaching
(CLT) gained prominence, some structures associated with
grammar started to be taught lexically (or functionally). I’d like
to is not taught as ‹the conditional› but as a chunk expressing
desire. Similarly many other ‹traditional› grammar items can
be introduced lexically relatively early on.
Less grammar or more grammar?
You are, no doubt, all familiar with students who on one hand seem to know the ‘rules’ of grammar but still fail to produce grammatically correct sentences when speaking or, on the other, sound unnatural and foreign-like even when their sentences are grammatically correct. Michael Lewis, who might be considered the founder of the Lexical Approach, once claimed that there was no direct relationship between the knowledge of grammar and speaking. In contrast, the knowledge of formulaic language has been shown by research to have a significant bearing on the natural language production.
Furthermore, certain grammar rules are practically impossible to learn. Dave Willis cites the grammar of orientation (which includes the notoriously difficult present perfect and the uses of certain modal verbs) as particularly resistant to teaching. The only way to grasp their meaning is through continuous exposure and use.
Finally, even the most authoritative English grammars never claim to provide a comprehensive description of all the grammar, hence the word ‘introduction’ often used in their titles (for instance, Huddleston & Pullum’s A Student’s Introduction to English Grammar or Halliday’s An Introduction to Functional Grammar).
If grammarians do not even attempt to address all areas of grammar, how can we, practitioners, cover all the aspects of grammar in our teaching, especially if all we seem to focus on is a limited selection of discrete items, comprised mostly of tenses and a handful of modal verbs? It would seem that we need to expose our students to a lot of naturally occurring language and frequently draw their attention to various grammar points as they arise.
For example, while teaching the expression fall asleep / be asleep you can ask your students:
• Don’t make any noise – she’s fallen asleep.
• Don’t make any noise – she’s asleep.
What does’s stand for in each of these cases (is or has)?
One of the fathers of the Communicative Language Teaching Henry Widdowson advocated using lexical items as a starting point and then ‘showing how they need to be grammatically modified to be communicatively effective’ (1990:95). For example, when exploring a text with your students, you may come across a sentence like this:
• They’ve been married for seven years.
You can ask your students: When did they get married? How should you change the sentence if the couple you are talking about is no longer married?
The above demonstrates how the teacher should be constantly on the ball and take every opportunity to draw students’ attention to grammar. Such short but frequent ‘grammar spots’ will help to slowly raise students’ awareness and build their understanding of the English grammar system.
[…]
Conclusion
So is there room for grammar instruction in the classroom? Certainly yes. But the grammar practice should always start with the exploitation of lexical items. Exposing students to a lot of natural and contextualised examples will offer a lexical way into the grammar of the language.
To sum up, grammar should play some role in language teaching but should not occupy a big part of class time. Instead grammar should be delivered in small but frequent portions. Students should be encouraged to collect a lot of examples of a particular structure before being invited to analyse it. Hence, analysis should be preceded by synthesis.
Lastly, language practitioners should bear in mind that grammar acquisition is an incremental process which requires frequent focus and refocus on the items already studied.
Available at: https://www.teachingenglish.org.uk/professionaldevelopment/teachers/knowing-subject/articles/grammar-vs-lexisor-grammar-through. Accessed on: April 29, 2024.
Read the following text to answer the question.
By Leo Selivan
In this article, informed by the Lexical Approach, I reflect on grammar instruction in the classroom […]. I consider the problems with ‘traditional’ grammar teaching before arguing that what we actually need is more grammar input as well as showing how lexis can provide necessary ‘crutches’ for the learner.
Lexis = vocabulary + grammar
The shift in ELT from grammar to lexis mirrors a similar change in the attitude of linguists. In the past linguists were preoccupied with the grammar of language; however the advances in corpus linguistics have pushed lexis to the forefront. The term ‘lexis’, which was traditionally used by linguists, is a common word these days and frequently used even in textbooks.
Why use a technical term borrowed from the realm of linguistics instead of the word ‘vocabulary’? Quite simply because vocabulary is typically seen as individual words (often presented in lists) whereas lexis is a somewhat wider concept and consists of collocations, chunks and formulaic expressions. It also includes certain patterns that were traditionally associated with the grammar of a language, e.g. If I were you…, I haven’t seen you for ages etc.
Recognising certain grammar structures as lexical
items means that they can be introduced much earlier,
without structural analysis or elaboration. Indeed, since the
concept of notions and functions made its way into language
teaching, particularly as Communicative Language Teaching
(CLT) gained prominence, some structures associated with
grammar started to be taught lexically (or functionally). I’d like
to is not taught as ‹the conditional› but as a chunk expressing
desire. Similarly many other ‹traditional› grammar items can
be introduced lexically relatively early on.
Less grammar or more grammar?
You are, no doubt, all familiar with students who on one hand seem to know the ‘rules’ of grammar but still fail to produce grammatically correct sentences when speaking or, on the other, sound unnatural and foreign-like even when their sentences are grammatically correct. Michael Lewis, who might be considered the founder of the Lexical Approach, once claimed that there was no direct relationship between the knowledge of grammar and speaking. In contrast, the knowledge of formulaic language has been shown by research to have a significant bearing on the natural language production.
Furthermore, certain grammar rules are practically impossible to learn. Dave Willis cites the grammar of orientation (which includes the notoriously difficult present perfect and the uses of certain modal verbs) as particularly resistant to teaching. The only way to grasp their meaning is through continuous exposure and use.
Finally, even the most authoritative English grammars never claim to provide a comprehensive description of all the grammar, hence the word ‘introduction’ often used in their titles (for instance, Huddleston & Pullum’s A Student’s Introduction to English Grammar or Halliday’s An Introduction to Functional Grammar).
If grammarians do not even attempt to address all areas of grammar, how can we, practitioners, cover all the aspects of grammar in our teaching, especially if all we seem to focus on is a limited selection of discrete items, comprised mostly of tenses and a handful of modal verbs? It would seem that we need to expose our students to a lot of naturally occurring language and frequently draw their attention to various grammar points as they arise.
For example, while teaching the expression fall asleep / be asleep you can ask your students:
• Don’t make any noise – she’s fallen asleep.
• Don’t make any noise – she’s asleep.
What does’s stand for in each of these cases (is or has)?
One of the fathers of the Communicative Language Teaching Henry Widdowson advocated using lexical items as a starting point and then ‘showing how they need to be grammatically modified to be communicatively effective’ (1990:95). For example, when exploring a text with your students, you may come across a sentence like this:
• They’ve been married for seven years.
You can ask your students: When did they get married? How should you change the sentence if the couple you are talking about is no longer married?
The above demonstrates how the teacher should be constantly on the ball and take every opportunity to draw students’ attention to grammar. Such short but frequent ‘grammar spots’ will help to slowly raise students’ awareness and build their understanding of the English grammar system.
[…]
Conclusion
So is there room for grammar instruction in the classroom? Certainly yes. But the grammar practice should always start with the exploitation of lexical items. Exposing students to a lot of natural and contextualised examples will offer a lexical way into the grammar of the language.
To sum up, grammar should play some role in language teaching but should not occupy a big part of class time. Instead grammar should be delivered in small but frequent portions. Students should be encouraged to collect a lot of examples of a particular structure before being invited to analyse it. Hence, analysis should be preceded by synthesis.
Lastly, language practitioners should bear in mind that grammar acquisition is an incremental process which requires frequent focus and refocus on the items already studied.
Available at: https://www.teachingenglish.org.uk/professionaldevelopment/teachers/knowing-subject/articles/grammar-vs-lexisor-grammar-through. Accessed on: April 29, 2024.
Read the following text to answer the question.
By Leo Selivan
In this article, informed by the Lexical Approach, I reflect on grammar instruction in the classroom […]. I consider the problems with ‘traditional’ grammar teaching before arguing that what we actually need is more grammar input as well as showing how lexis can provide necessary ‘crutches’ for the learner.
Lexis = vocabulary + grammar
The shift in ELT from grammar to lexis mirrors a similar change in the attitude of linguists. In the past linguists were preoccupied with the grammar of language; however the advances in corpus linguistics have pushed lexis to the forefront. The term ‘lexis’, which was traditionally used by linguists, is a common word these days and frequently used even in textbooks.
Why use a technical term borrowed from the realm of linguistics instead of the word ‘vocabulary’? Quite simply because vocabulary is typically seen as individual words (often presented in lists) whereas lexis is a somewhat wider concept and consists of collocations, chunks and formulaic expressions. It also includes certain patterns that were traditionally associated with the grammar of a language, e.g. If I were you…, I haven’t seen you for ages etc.
Recognising certain grammar structures as lexical
items means that they can be introduced much earlier,
without structural analysis or elaboration. Indeed, since the
concept of notions and functions made its way into language
teaching, particularly as Communicative Language Teaching
(CLT) gained prominence, some structures associated with
grammar started to be taught lexically (or functionally). I’d like
to is not taught as ‹the conditional› but as a chunk expressing
desire. Similarly many other ‹traditional› grammar items can
be introduced lexically relatively early on.
Less grammar or more grammar?
You are, no doubt, all familiar with students who on one hand seem to know the ‘rules’ of grammar but still fail to produce grammatically correct sentences when speaking or, on the other, sound unnatural and foreign-like even when their sentences are grammatically correct. Michael Lewis, who might be considered the founder of the Lexical Approach, once claimed that there was no direct relationship between the knowledge of grammar and speaking. In contrast, the knowledge of formulaic language has been shown by research to have a significant bearing on the natural language production.
Furthermore, certain grammar rules are practically impossible to learn. Dave Willis cites the grammar of orientation (which includes the notoriously difficult present perfect and the uses of certain modal verbs) as particularly resistant to teaching. The only way to grasp their meaning is through continuous exposure and use.
Finally, even the most authoritative English grammars never claim to provide a comprehensive description of all the grammar, hence the word ‘introduction’ often used in their titles (for instance, Huddleston & Pullum’s A Student’s Introduction to English Grammar or Halliday’s An Introduction to Functional Grammar).
If grammarians do not even attempt to address all areas of grammar, how can we, practitioners, cover all the aspects of grammar in our teaching, especially if all we seem to focus on is a limited selection of discrete items, comprised mostly of tenses and a handful of modal verbs? It would seem that we need to expose our students to a lot of naturally occurring language and frequently draw their attention to various grammar points as they arise.
For example, while teaching the expression fall asleep / be asleep you can ask your students:
• Don’t make any noise – she’s fallen asleep.
• Don’t make any noise – she’s asleep.
What does’s stand for in each of these cases (is or has)?
One of the fathers of the Communicative Language Teaching Henry Widdowson advocated using lexical items as a starting point and then ‘showing how they need to be grammatically modified to be communicatively effective’ (1990:95). For example, when exploring a text with your students, you may come across a sentence like this:
• They’ve been married for seven years.
You can ask your students: When did they get married? How should you change the sentence if the couple you are talking about is no longer married?
The above demonstrates how the teacher should be constantly on the ball and take every opportunity to draw students’ attention to grammar. Such short but frequent ‘grammar spots’ will help to slowly raise students’ awareness and build their understanding of the English grammar system.
[…]
Conclusion
So is there room for grammar instruction in the classroom? Certainly yes. But the grammar practice should always start with the exploitation of lexical items. Exposing students to a lot of natural and contextualised examples will offer a lexical way into the grammar of the language.
To sum up, grammar should play some role in language teaching but should not occupy a big part of class time. Instead grammar should be delivered in small but frequent portions. Students should be encouraged to collect a lot of examples of a particular structure before being invited to analyse it. Hence, analysis should be preceded by synthesis.
Lastly, language practitioners should bear in mind that grammar acquisition is an incremental process which requires frequent focus and refocus on the items already studied.
Available at: https://www.teachingenglish.org.uk/professionaldevelopment/teachers/knowing-subject/articles/grammar-vs-lexisor-grammar-through. Accessed on: April 29, 2024.
Read the following text to answer the question.
By Leo Selivan
In this article, informed by the Lexical Approach, I reflect on grammar instruction in the classroom […]. I consider the problems with ‘traditional’ grammar teaching before arguing that what we actually need is more grammar input as well as showing how lexis can provide necessary ‘crutches’ for the learner.
Lexis = vocabulary + grammar
The shift in ELT from grammar to lexis mirrors a similar change in the attitude of linguists. In the past linguists were preoccupied with the grammar of language; however the advances in corpus linguistics have pushed lexis to the forefront. The term ‘lexis’, which was traditionally used by linguists, is a common word these days and frequently used even in textbooks.
Why use a technical term borrowed from the realm of linguistics instead of the word ‘vocabulary’? Quite simply because vocabulary is typically seen as individual words (often presented in lists) whereas lexis is a somewhat wider concept and consists of collocations, chunks and formulaic expressions. It also includes certain patterns that were traditionally associated with the grammar of a language, e.g. If I were you…, I haven’t seen you for ages etc.
Recognising certain grammar structures as lexical
items means that they can be introduced much earlier,
without structural analysis or elaboration. Indeed, since the
concept of notions and functions made its way into language
teaching, particularly as Communicative Language Teaching
(CLT) gained prominence, some structures associated with
grammar started to be taught lexically (or functionally). I’d like
to is not taught as ‹the conditional› but as a chunk expressing
desire. Similarly many other ‹traditional› grammar items can
be introduced lexically relatively early on.
Less grammar or more grammar?
You are, no doubt, all familiar with students who on one hand seem to know the ‘rules’ of grammar but still fail to produce grammatically correct sentences when speaking or, on the other, sound unnatural and foreign-like even when their sentences are grammatically correct. Michael Lewis, who might be considered the founder of the Lexical Approach, once claimed that there was no direct relationship between the knowledge of grammar and speaking. In contrast, the knowledge of formulaic language has been shown by research to have a significant bearing on the natural language production.
Furthermore, certain grammar rules are practically impossible to learn. Dave Willis cites the grammar of orientation (which includes the notoriously difficult present perfect and the uses of certain modal verbs) as particularly resistant to teaching. The only way to grasp their meaning is through continuous exposure and use.
Finally, even the most authoritative English grammars never claim to provide a comprehensive description of all the grammar, hence the word ‘introduction’ often used in their titles (for instance, Huddleston & Pullum’s A Student’s Introduction to English Grammar or Halliday’s An Introduction to Functional Grammar).
If grammarians do not even attempt to address all areas of grammar, how can we, practitioners, cover all the aspects of grammar in our teaching, especially if all we seem to focus on is a limited selection of discrete items, comprised mostly of tenses and a handful of modal verbs? It would seem that we need to expose our students to a lot of naturally occurring language and frequently draw their attention to various grammar points as they arise.
For example, while teaching the expression fall asleep / be asleep you can ask your students:
• Don’t make any noise – she’s fallen asleep.
• Don’t make any noise – she’s asleep.
What does’s stand for in each of these cases (is or has)?
One of the fathers of the Communicative Language Teaching Henry Widdowson advocated using lexical items as a starting point and then ‘showing how they need to be grammatically modified to be communicatively effective’ (1990:95). For example, when exploring a text with your students, you may come across a sentence like this:
• They’ve been married for seven years.
You can ask your students: When did they get married? How should you change the sentence if the couple you are talking about is no longer married?
The above demonstrates how the teacher should be constantly on the ball and take every opportunity to draw students’ attention to grammar. Such short but frequent ‘grammar spots’ will help to slowly raise students’ awareness and build their understanding of the English grammar system.
[…]
Conclusion
So is there room for grammar instruction in the classroom? Certainly yes. But the grammar practice should always start with the exploitation of lexical items. Exposing students to a lot of natural and contextualised examples will offer a lexical way into the grammar of the language.
To sum up, grammar should play some role in language teaching but should not occupy a big part of class time. Instead grammar should be delivered in small but frequent portions. Students should be encouraged to collect a lot of examples of a particular structure before being invited to analyse it. Hence, analysis should be preceded by synthesis.
Lastly, language practitioners should bear in mind that grammar acquisition is an incremental process which requires frequent focus and refocus on the items already studied.
Available at: https://www.teachingenglish.org.uk/professionaldevelopment/teachers/knowing-subject/articles/grammar-vs-lexisor-grammar-through. Accessed on: April 29, 2024.
Empowering language learning through assessment
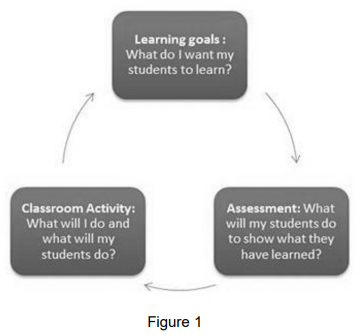
Assessment of, as, and for learning
Leia as afirmativas a seguir:
I. Na frase “i took a swim” ocorre um verbo que pode ser melhor traduzido como correr.
II. O aprendizado de uma língua estrangeira deve possibilitar que o aluno, ao se envolver nos processos de construir significados nessa língua, se constitua em um ser discursivo no uso de uma língua estrangeira.
Marque a alternativa CORRETA:
Leia as afirmativas a seguir:
I. Ocorre verbo na frase: we ran through the whole town in search of the book.
II. Ocorre verbo na frase: the stone travelled the air.
Marque a alternativa CORRETA:
Leia as afirmativas a seguir:
I. Ao ensinar uma língua estrangeira, é essencial uma compreensão teórica do que é a linguagem, tanto do ponto de vista dos conhecimentos necessários para usá-la quanto em relação ao uso que fazem desses conhecimentos para construir significados no mundo social.
II. Na frase “he eats him out of house and home”, o verbo 'eats' pode ser melhor traduzido como reformar.
Marque a alternativa CORRETA:
“A ___________________________________ é realizada com o propósito de informar o professor e o aluno sobre o resultado da aprendizagem, durante o desenvolvimento das atividades escolares. Localiza deficiências na organização do ensino-aprendizagem de modo a possibilitar reformulações no mesmo e assegurar o alcance dos objetivos.”
Leia o texto abaixo e escolha a alternativa sobre a qual método de ensino ele se refere:
O método ensina tudo, passo a passo, numa ordem hierarquicamente estabelecida, do mais fácil para o mais difícil. O aluno, seja ele quem for, parte de um ponto inicial zero, igual para todos, e vai progredindo, através dos elementos já dominados, de maneira lógica e ordenada. A todo instante, feitos testes de avaliação (ditados, exercícios estruturais, leitura perante a classe), para que o professor avalie se o aluno “acompanha” ou se ficou para trás. Neste último caso, tudo é repetido de novo, para ver se o aluno, desta vez, aprende. Se ainda assim não aprender, repete-se mais uma vez, remanejam-se os alunos atrasados para uma classe especial, para não atrapalharem os que progrediram, até que o aluno, à força de ficar reprovado, desista de estudar, julgando-se incapaz. E a escola lamenta a chance que a criança teve e que não soube aproveitar.
A LDB dispõe que, exceto os estabelecimentos de ensino, respeitadas as normas comuns e as do seu sistema de ensino, terão a incumbência de:
I- Elaborar e executar sua proposta pedagógica;
II- Administrar seu pessoal e seus recursos materiais e financeiros;
III- Assegurar o cumprimento dos dias letivos e horas-aula estabelecidas;
IV- Velar pelo cumprimento do plano de trabalho de cada docente;
V- Prover meios para a recuperação dos alunos de menor rendimento;
VI- Zelar pela aprendizagem dos alunos.
Analyze the following sentence.
"What is your name?" He asked me.
Put this sentence in the reported speech.
Analyze the following sentence.
Ana says: “I’m going to work until 6 p.m”.
Put this sentence in the reported speech.
Fill in the blanks with the correct form of the verbs.
This is the best vacation we ______ (ever have).
I have _______ such a beautiful baby (never see).
A great opportunity ______ (have been / miss).
Select the CORRECT answer.
Fill in the blanks with many, much, a lot of, a few, a little.
______ people.
______ patience.
______ time.
______ chairs.
Select the CORRECT answer.
Fill in the blanks with for or since.
I don’t sleep ________ Friday.
They didn't drink ________ last night.
He didn’t shower _________ days.
It has been snowing ______ Wednesday.
Select the CORRECT answer.