Questões de Concurso
Para analista de redes e comunicação de dados
Foram encontradas 1.919 questões
Resolva questões gratuitamente!
Junte-se a mais de 4 milhões de concurseiros!

Tomando por base o texto acima, julgue os itens.
O uso da conjunção “ou” (L.15) mostra que, no texto, estar “inserido nas principais discussões em curso no mundo” (L.14-15) ou “adquirir apenas uma visão geral das grandes questões do ser humano na atualidade” (L.16-17) devem ser interpretadas como duas maneiras diferentes de se expressar lingüisticamente a mesma ação.
Deixo 1/3 da quantia que tenho no Banco à minha única filha, Minerva, e o restante à criança que ela está esperando, caso seja do sexo feminino; entretanto, se a criança que ela espera for do sexo masculino, tal quantia deverá ser igualmente dividida entre os dois.”
Considerando que, 1 mês após o falecimento de Astolfo, Minerva teve um casal de gêmeos, então, para que o testamento de Astolfo fosse atendido, as frações da quantia existente no Banco, recebidas por Minerva, seu filho e sua filha foram, respectivamente:
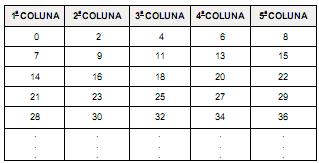
Se esse padrão fosse mantido indefinidamente, qual dos números seguintes com certeza NÃO estaria nessa tabela?
Sometimes it looks like the IT revolution has moved on and left many IS researchers [ADVERB].
For example, according to Nokia, the next generation of computers will be in your pocket. About 1.3 billion mobile phones are sold each year, compared to only 300 million personal computers. An increasing number of these phones come with full-blown operating systems that let users access, organize, and use much more information than older handhelds. The mobile software market may soon exceed the current software market for computers, and a wide variety of information systems will rise on top of all the new software. However, only a relatively small percentage of IS research focuses on the mobile revolution.
Actually, many IS programs in business colleges seem impervious to the wake-up call that information schools provide. Rather, they continue to offer curricula that reflect the past rather than look toward the future. Little wonder that students, whose degrees are based on a very limited number of traditional courses in one area of study, often fail to meet their employers' expectations. With little integration across disciplines to prepare students for the complex problems they will face, organizations
find it necessary to further educate those whom they hire or go abroad to seek appropriate employees with a wider range of skills and knowledge.
(Adapted from
http://www.computer.org/cms/Computer.org/ComputingNow/hom
epage/2009/1009/rW_CO_ISInnovation.pdf)
Harry McCracken, PC World
Monday, October 19, 2009 10:00 AM PDT
Reading about a new operating system can tell you only so much about it: After all, Windows Vista had far more features than XP, [CONJUNCTION] fell far short of it in the eyes of many users. To judge an OS accurately, you have to live with it. Over the past ten months, I've spent a substantial percentage of my computing life in Windows 7, starting with a preliminary version and culminating in recent weeks with the final Release to Manufacturing edition. I've run it on systems ranging from an underpowered Asus EeePC 1000HE netbook to a potent HP TouchSmart all-in-one. And I've used it to do real work, not lab routines. Usually, I've run the OS in multiboot configurations with Windows Vista and/or XP, so I've had a choice each time I turned the computer on: [MODAL] I opt for Windows 7 or an
older version of the OS? The call has been easy to make, because Win 7 is so pleasant to use.
So why wouldn't you want to run this operating system? Concern over its performance is one logical reason, especially since early versions of Windows Vista managed to turn PCs that ran XP with ease into lethargic underperformers. The PC World Test Center's speed benchmarks on five test PCs showed Windows 7 to be faster than Vista, but only by a little; I've found it to be reasonably quick on every computer I've used it on - even the Asus netbook, once I upgraded it to 2GB of RAM. (Our lab tried Win 7 on a Lenovo S10 netbook with 1GB of RAM and found it to be a shade slower than XP; for details see "Windows 7 Performance Tests.").
Here's a rule of thumb that errs on the side of caution: If your PC's specs qualify it to run Vista, get Windows 7; if they don't, avoid it. Microsoft's official hardware configuration requirements for Windows 7 are nearly identical to those it recommends for Windows Vista: a 1-GHz CPU, 1GB of RAM,
16GB of free disk space, and a DirectX 9-compatible graphics device with a WDDM 1.0 or higher driver. That's for the 32-bit version of Windows 7; the 64-bit version of the OS requires a 64-bit CPU, 2GB of RAM, and 20GB of disk space.
Fear of incompatible hardware and software is another understandable reason to be wary of Windows 7. One unfortunate law of operating-system upgrades - which applies equally to Macs and to Windows PCs - is that they will break some systems and applications, especially at first.
Under the hood, Windows 7 isn't radically different from Vista. That's a plus, since it should greatly reduce the volume of difficulties relating to drivers and apps compared to Vista's bumpy rollout. I have performed a half-dozen Windows 7 upgrades, and most of them went off without a hitch. The
gnarliest problem arose when I had to track down a graphics driver for Dell's XPS M1330 laptop on my own - Windows 7 installed a generic VGA driver that couldn't run the Aero user interface, and as a result failed to support new Windows 7 features such as thumbnail views in the Taskbar.
The best way to reduce your odds of running into a showstopping problem with Windows 7 is to bide your time. When the new operating system arrives on October 22, sit back and let the earliest adopters discover the worst snafus. Within a few weeks, Microsoft and other software and hardware companies will have fixed most of them, and your chances of a happy migration to Win 7 will be much higher. If you want to be really conservative, hold off on moving to Win 7 until you're ready to buy a PC that's designed to run it well.
Waiting a bit before making the leap makes sense; waiting forever does not. Microsoft took far too long to come up with a satisfactory replacement for Windows XP. But whether you choose to install Windows 7 on your current systems or get it on the next new PC you buy, you'll find that it's the unassuming, thoroughly practical upgrade you've been waiting for ? flaws and all.
(Adapted from http://www.pcworld.com/article/172602/windows_7_revi...)
Harry McCracken, PC World
Monday, October 19, 2009 10:00 AM PDT
Reading about a new operating system can tell you only so much about it: After all, Windows Vista had far more features than XP, [CONJUNCTION] fell far short of it in the eyes of many users. To judge an OS accurately, you have to live with it. Over the past ten months, I've spent a substantial percentage of my computing life in Windows 7, starting with a preliminary version and culminating in recent weeks with the final Release to Manufacturing edition. I've run it on systems ranging from an underpowered Asus EeePC 1000HE netbook to a potent HP TouchSmart all-in-one. And I've used it to do real work, not lab routines. Usually, I've run the OS in multiboot configurations with Windows Vista and/or XP, so I've had a choice each time I turned the computer on: [MODAL] I opt for Windows 7 or an
older version of the OS? The call has been easy to make, because Win 7 is so pleasant to use.
So why wouldn't you want to run this operating system? Concern over its performance is one logical reason, especially since early versions of Windows Vista managed to turn PCs that ran XP with ease into lethargic underperformers. The PC World Test Center's speed benchmarks on five test PCs showed Windows 7 to be faster than Vista, but only by a little; I've found it to be reasonably quick on every computer I've used it on - even the Asus netbook, once I upgraded it to 2GB of RAM. (Our lab tried Win 7 on a Lenovo S10 netbook with 1GB of RAM and found it to be a shade slower than XP; for details see "Windows 7 Performance Tests.").
Here's a rule of thumb that errs on the side of caution: If your PC's specs qualify it to run Vista, get Windows 7; if they don't, avoid it. Microsoft's official hardware configuration requirements for Windows 7 are nearly identical to those it recommends for Windows Vista: a 1-GHz CPU, 1GB of RAM,
16GB of free disk space, and a DirectX 9-compatible graphics device with a WDDM 1.0 or higher driver. That's for the 32-bit version of Windows 7; the 64-bit version of the OS requires a 64-bit CPU, 2GB of RAM, and 20GB of disk space.
Fear of incompatible hardware and software is another understandable reason to be wary of Windows 7. One unfortunate law of operating-system upgrades - which applies equally to Macs and to Windows PCs - is that they will break some systems and applications, especially at first.
Under the hood, Windows 7 isn't radically different from Vista. That's a plus, since it should greatly reduce the volume of difficulties relating to drivers and apps compared to Vista's bumpy rollout. I have performed a half-dozen Windows 7 upgrades, and most of them went off without a hitch. The
gnarliest problem arose when I had to track down a graphics driver for Dell's XPS M1330 laptop on my own - Windows 7 installed a generic VGA driver that couldn't run the Aero user interface, and as a result failed to support new Windows 7 features such as thumbnail views in the Taskbar.
The best way to reduce your odds of running into a showstopping problem with Windows 7 is to bide your time. When the new operating system arrives on October 22, sit back and let the earliest adopters discover the worst snafus. Within a few weeks, Microsoft and other software and hardware companies will have fixed most of them, and your chances of a happy migration to Win 7 will be much higher. If you want to be really conservative, hold off on moving to Win 7 until you're ready to buy a PC that's designed to run it well.
Waiting a bit before making the leap makes sense; waiting forever does not. Microsoft took far too long to come up with a satisfactory replacement for Windows XP. But whether you choose to install Windows 7 on your current systems or get it on the next new PC you buy, you'll find that it's the unassuming, thoroughly practical upgrade you've been waiting for ? flaws and all.
(Adapted from http://www.pcworld.com/article/172602/windows_7_revi...)
Harry McCracken, PC World
Monday, October 19, 2009 10:00 AM PDT
Reading about a new operating system can tell you only so much about it: After all, Windows Vista had far more features than XP, [CONJUNCTION] fell far short of it in the eyes of many users. To judge an OS accurately, you have to live with it. Over the past ten months, I've spent a substantial percentage of my computing life in Windows 7, starting with a preliminary version and culminating in recent weeks with the final Release to Manufacturing edition. I've run it on systems ranging from an underpowered Asus EeePC 1000HE netbook to a potent HP TouchSmart all-in-one. And I've used it to do real work, not lab routines. Usually, I've run the OS in multiboot configurations with Windows Vista and/or XP, so I've had a choice each time I turned the computer on: [MODAL] I opt for Windows 7 or an
older version of the OS? The call has been easy to make, because Win 7 is so pleasant to use.
So why wouldn't you want to run this operating system? Concern over its performance is one logical reason, especially since early versions of Windows Vista managed to turn PCs that ran XP with ease into lethargic underperformers. The PC World Test Center's speed benchmarks on five test PCs showed Windows 7 to be faster than Vista, but only by a little; I've found it to be reasonably quick on every computer I've used it on - even the Asus netbook, once I upgraded it to 2GB of RAM. (Our lab tried Win 7 on a Lenovo S10 netbook with 1GB of RAM and found it to be a shade slower than XP; for details see "Windows 7 Performance Tests.").
Here's a rule of thumb that errs on the side of caution: If your PC's specs qualify it to run Vista, get Windows 7; if they don't, avoid it. Microsoft's official hardware configuration requirements for Windows 7 are nearly identical to those it recommends for Windows Vista: a 1-GHz CPU, 1GB of RAM,
16GB of free disk space, and a DirectX 9-compatible graphics device with a WDDM 1.0 or higher driver. That's for the 32-bit version of Windows 7; the 64-bit version of the OS requires a 64-bit CPU, 2GB of RAM, and 20GB of disk space.
Fear of incompatible hardware and software is another understandable reason to be wary of Windows 7. One unfortunate law of operating-system upgrades - which applies equally to Macs and to Windows PCs - is that they will break some systems and applications, especially at first.
Under the hood, Windows 7 isn't radically different from Vista. That's a plus, since it should greatly reduce the volume of difficulties relating to drivers and apps compared to Vista's bumpy rollout. I have performed a half-dozen Windows 7 upgrades, and most of them went off without a hitch. The
gnarliest problem arose when I had to track down a graphics driver for Dell's XPS M1330 laptop on my own - Windows 7 installed a generic VGA driver that couldn't run the Aero user interface, and as a result failed to support new Windows 7 features such as thumbnail views in the Taskbar.
The best way to reduce your odds of running into a showstopping problem with Windows 7 is to bide your time. When the new operating system arrives on October 22, sit back and let the earliest adopters discover the worst snafus. Within a few weeks, Microsoft and other software and hardware companies will have fixed most of them, and your chances of a happy migration to Win 7 will be much higher. If you want to be really conservative, hold off on moving to Win 7 until you're ready to buy a PC that's designed to run it well.
Waiting a bit before making the leap makes sense; waiting forever does not. Microsoft took far too long to come up with a satisfactory replacement for Windows XP. But whether you choose to install Windows 7 on your current systems or get it on the next new PC you buy, you'll find that it's the unassuming, thoroughly practical upgrade you've been waiting for ? flaws and all.
(Adapted from http://www.pcworld.com/article/172602/windows_7_revi...)
Se examinarmos as fábulas populares, verificaremos que elas representam dois tipos de transformação social, sempre com final feliz. Num primeiro tipo, existe um príncipe que, por alguma
circunstância, se vê reduzido a guardador de porcos ou alguma outra condição miserável, para depois reconquistar sua condição real. Num segundo caso, existe um jovem pastor que não possuiu nada desde o nascimento e que, por virtude própria ou graça do destino, consegue se casar com a princesa e tornar-se rei.
Os mesmos esquemas valem para as protagonistas femininas: a donzela nobre é vítima de uma madrasta (Branca de Neve) ou de irmãs invejosas (Cinderela), até que um príncipe se apaixone por ela e a conduza ao vértice da escala social. Ou então uma camponesa pobre supera todas as desvantagens da origem e realiza núpcias principescas.
Poderíamos pensar que as fábulas do segundo tipo são as que exprimem mais diretamente o desejo popular de uma reviravolta dos papéis sociais e dos destinos individuais, ao passo que as do primeiro tipo deixam aparecer tal desejo de forma mais atenuada, como restauração de uma hipotética ordem precedente. Mas, pensando bem, os destinos extraordinários do pastorzinho ou da camponesa representam apenas uma ilusão miraculosa e consoladora, ao passo que os infortúnios do príncipe
ou da jovem nobre associam a imagem da pobreza com a ideia de um direito subtraído, de uma justiça a ser reivindicada, isto é, estabelecem no plano da fantasia um ponto que será fundamental para toda tomada de consciência da época moderna, da Revolução Francesa em diante.
No inconsciente coletivo, o príncipe disfarçado de pobre é a prova de que cada pobre é, na realidade, um príncipe que sofreu uma usurpação de poder e por isso deve reconquistar seu reino. Quando cavaleiros caídos em desgraça triunfarem sobre seus inimigos, hão de restaurar uma sociedade mais justa, na qual será reconhecida sua verdadeira identidade.
(Adaptado de Ítalo Calvino, Por que ler os clássicos)
Se examinarmos as fábulas populares, verificaremos que elas representam dois tipos de transformação social, sempre com final feliz. Num primeiro tipo, existe um príncipe que, por alguma
circunstância, se vê reduzido a guardador de porcos ou alguma outra condição miserável, para depois reconquistar sua condição real. Num segundo caso, existe um jovem pastor que não possuiu nada desde o nascimento e que, por virtude própria ou graça do destino, consegue se casar com a princesa e tornar-se rei.
Os mesmos esquemas valem para as protagonistas femininas: a donzela nobre é vítima de uma madrasta (Branca de Neve) ou de irmãs invejosas (Cinderela), até que um príncipe se apaixone por ela e a conduza ao vértice da escala social. Ou então uma camponesa pobre supera todas as desvantagens da origem e realiza núpcias principescas.
Poderíamos pensar que as fábulas do segundo tipo são as que exprimem mais diretamente o desejo popular de uma reviravolta dos papéis sociais e dos destinos individuais, ao passo que as do primeiro tipo deixam aparecer tal desejo de forma mais atenuada, como restauração de uma hipotética ordem precedente. Mas, pensando bem, os destinos extraordinários do pastorzinho ou da camponesa representam apenas uma ilusão miraculosa e consoladora, ao passo que os infortúnios do príncipe
ou da jovem nobre associam a imagem da pobreza com a ideia de um direito subtraído, de uma justiça a ser reivindicada, isto é, estabelecem no plano da fantasia um ponto que será fundamental para toda tomada de consciência da época moderna, da Revolução Francesa em diante.
No inconsciente coletivo, o príncipe disfarçado de pobre é a prova de que cada pobre é, na realidade, um príncipe que sofreu uma usurpação de poder e por isso deve reconquistar seu reino. Quando cavaleiros caídos em desgraça triunfarem sobre seus inimigos, hão de restaurar uma sociedade mais justa, na qual será reconhecida sua verdadeira identidade.
(Adaptado de Ítalo Calvino, Por que ler os clássicos)
Das informações do texto conclui-se que o intercâmbio de dados e informações entre agências de inteligência coíbe a expansão de redes criminosas.
A supressão das vírgulas que isolam a expressão “da Secretaria Nacional de Segurança Pública” (L.10-11) alteraria o sentido do texto, visto que estaria subentendida a existência de, pelo menos, mais um projeto denominado Segurança Pública para o Brasil.
Estaria gramaticalmente correto o emprego da preposição a antes de “toda a população” (L.6) — a toda a população — visto que a forma verbal “afetam” (L.5) apresenta dupla regência.

Com base nas informações acima, julgue o item a seguir
A solução do sistema de equações lineares 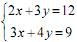 fornece, de fato, uma possível quantidade a ser produzida de P1 e P2.
fornece, de fato, uma possível quantidade a ser produzida de P1 e P2.

Com referência às estruturas linguísticas empregadas no texto,
julgue os itens subsequentes.
normalmente utilizados em uma SAN, julgue os itens que se
seguem.
normalmente utilizados em uma SAN, julgue os itens que se
seguem.

Considerando o trecho de código acima, no formato de shell script,
julgue os itens a seguir.
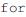 , do código acima, o dado lido e inicialmente armazenado em
, do código acima, o dado lido e inicialmente armazenado em 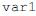 é transferido para a variável
é transferido para a variável 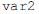 e as letras minúsculas transformadas em maiúsculas.
e as letras minúsculas transformadas em maiúsculas.

