Questões de Concurso
Sobre interpretação de texto | reading comprehension em inglês
Foram encontradas 9.443 questões

Considere a figura e o texto a seguir, para responder a questão.
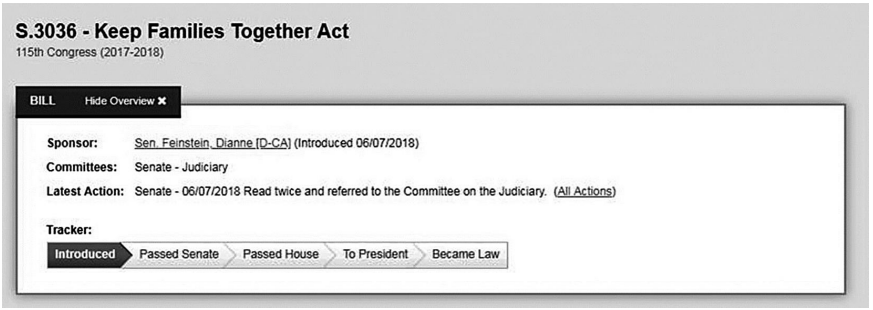
Keep Families Together Act
Considere a figura e o texto a seguir, para responder a questão.

Keep Families Together Act
Education
Education encompasses both the teaching and learning of knowledge, proper conduct, and technical competency. It thus focuses on the cultivation of skills, trades or professions, as well as mental, moral & aesthetic development.
Formal education consists of systematic instruction, teaching and training by professional teachers. This consists of the application of pedagogy and the development of curricula.
The right to education is a fundamental human right. Since 1952, Article 2 of the first Protocol to the European Convention on Human Rights obliges all signatory parties to guarantee the right to education. At world level, the United Nations’ International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights of 1966 guarantees this right under its Article 13.
Educational systems are established to provide education and training, often for children and the young. A curriculum defines what students should know, understand and be able to do as the result of education. A teaching profession delivers teaching which enables learning, and a system of policies, regulations, examinations, structures and funding enables teachers to teach to the best of their abilities.
Primary (or elementary) education consists of the first
years of formal, structured education. In general, primary education consists of six or seven years of schooling starting at the age of 5 or 6, although this varies
between, and sometimes within, countries. Globally,
around 70% of primary-age children are enrolled in
primary education, and this proportion is rising.
In most contemporary educational systems of the world, secondary education consists of the second years of formal education that occur during adolescence. It is characterized by transition from the typically compulsory, comprehensive primary education for minors, to the optional, selective tertiary, “post-secondary”, or “higher” education (e.g., university, vocational school) for adults.
Higher education, also called tertiary, third stage, or
post secondary education, is the non-compulsory
educational level that follows the completion of a
school providing a secondary education, such as a
high school or secondary school. Tertiary education is
normally taken to include undergraduate and postgraduate education, as well as vocational education and
training. Colleges and universities are the main institutions that provide tertiary education. Collectively,
these are sometimes known as tertiary institutions.
Tertiary education generally results in the receipt of
certificates, diplomas, or academic degrees.
Education
Education encompasses both the teaching and learning of knowledge, proper conduct, and technical competency. It thus focuses on the cultivation of skills, trades or professions, as well as mental, moral & aesthetic development.
Formal education consists of systematic instruction, teaching and training by professional teachers. This consists of the application of pedagogy and the development of curricula.
The right to education is a fundamental human right. Since 1952, Article 2 of the first Protocol to the European Convention on Human Rights obliges all signatory parties to guarantee the right to education. At world level, the United Nations’ International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights of 1966 guarantees this right under its Article 13.
Educational systems are established to provide education and training, often for children and the young. A curriculum defines what students should know, understand and be able to do as the result of education. A teaching profession delivers teaching which enables learning, and a system of policies, regulations, examinations, structures and funding enables teachers to teach to the best of their abilities.
Primary (or elementary) education consists of the first
years of formal, structured education. In general, primary education consists of six or seven years of schooling starting at the age of 5 or 6, although this varies
between, and sometimes within, countries. Globally,
around 70% of primary-age children are enrolled in
primary education, and this proportion is rising.
In most contemporary educational systems of the world, secondary education consists of the second years of formal education that occur during adolescence. It is characterized by transition from the typically compulsory, comprehensive primary education for minors, to the optional, selective tertiary, “post-secondary”, or “higher” education (e.g., university, vocational school) for adults.
Higher education, also called tertiary, third stage, or
post secondary education, is the non-compulsory
educational level that follows the completion of a
school providing a secondary education, such as a
high school or secondary school. Tertiary education is
normally taken to include undergraduate and postgraduate education, as well as vocational education and
training. Colleges and universities are the main institutions that provide tertiary education. Collectively,
these are sometimes known as tertiary institutions.
Tertiary education generally results in the receipt of
certificates, diplomas, or academic degrees.
Read the sentence below.
“The real life integration of language ........................... provides the teacher with a great deal of flexibility in ........................... motivated ............................”
Choose the alternative that correctly completes the
blank spaces in the sentence.
Education
Education encompasses both the teaching and learning of knowledge, proper conduct, and technical competency. It thus focuses on the cultivation of skills, trades or professions, as well as mental, moral & aesthetic development.
Formal education consists of systematic instruction, teaching and training by professional teachers. This consists of the application of pedagogy and the development of curricula.
The right to education is a fundamental human right. Since 1952, Article 2 of the first Protocol to the European Convention on Human Rights obliges all signatory parties to guarantee the right to education. At world level, the United Nations’ International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights of 1966 guarantees this right under its Article 13.
Educational systems are established to provide education and training, often for children and the young. A curriculum defines what students should know, understand and be able to do as the result of education. A teaching profession delivers teaching which enables learning, and a system of policies, regulations, examinations, structures and funding enables teachers to teach to the best of their abilities.
Primary (or elementary) education consists of the first
years of formal, structured education. In general, primary education consists of six or seven years of schooling starting at the age of 5 or 6, although this varies
between, and sometimes within, countries. Globally,
around 70% of primary-age children are enrolled in
primary education, and this proportion is rising.
In most contemporary educational systems of the world, secondary education consists of the second years of formal education that occur during adolescence. It is characterized by transition from the typically compulsory, comprehensive primary education for minors, to the optional, selective tertiary, “post-secondary”, or “higher” education (e.g., university, vocational school) for adults.
Higher education, also called tertiary, third stage, or
post secondary education, is the non-compulsory
educational level that follows the completion of a
school providing a secondary education, such as a
high school or secondary school. Tertiary education is
normally taken to include undergraduate and postgraduate education, as well as vocational education and
training. Colleges and universities are the main institutions that provide tertiary education. Collectively,
these are sometimes known as tertiary institutions.
Tertiary education generally results in the receipt of
certificates, diplomas, or academic degrees.
Education
Education encompasses both the teaching and learning of knowledge, proper conduct, and technical competency. It thus focuses on the cultivation of skills, trades or professions, as well as mental, moral & aesthetic development.
Formal education consists of systematic instruction, teaching and training by professional teachers. This consists of the application of pedagogy and the development of curricula.
The right to education is a fundamental human right. Since 1952, Article 2 of the first Protocol to the European Convention on Human Rights obliges all signatory parties to guarantee the right to education. At world level, the United Nations’ International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights of 1966 guarantees this right under its Article 13.
Educational systems are established to provide education and training, often for children and the young. A curriculum defines what students should know, understand and be able to do as the result of education. A teaching profession delivers teaching which enables learning, and a system of policies, regulations, examinations, structures and funding enables teachers to teach to the best of their abilities.
Primary (or elementary) education consists of the first
years of formal, structured education. In general, primary education consists of six or seven years of schooling starting at the age of 5 or 6, although this varies
between, and sometimes within, countries. Globally,
around 70% of primary-age children are enrolled in
primary education, and this proportion is rising.
In most contemporary educational systems of the world, secondary education consists of the second years of formal education that occur during adolescence. It is characterized by transition from the typically compulsory, comprehensive primary education for minors, to the optional, selective tertiary, “post-secondary”, or “higher” education (e.g., university, vocational school) for adults.
Higher education, also called tertiary, third stage, or
post secondary education, is the non-compulsory
educational level that follows the completion of a
school providing a secondary education, such as a
high school or secondary school. Tertiary education is
normally taken to include undergraduate and postgraduate education, as well as vocational education and
training. Colleges and universities are the main institutions that provide tertiary education. Collectively,
these are sometimes known as tertiary institutions.
Tertiary education generally results in the receipt of
certificates, diplomas, or academic degrees.
Learning a foreign language demands the development of some skills.
Choose the alternative that contains all of them.
Education
Education encompasses both the teaching and learning of knowledge, proper conduct, and technical competency. It thus focuses on the cultivation of skills, trades or professions, as well as mental, moral & aesthetic development.
Formal education consists of systematic instruction, teaching and training by professional teachers. This consists of the application of pedagogy and the development of curricula.
The right to education is a fundamental human right. Since 1952, Article 2 of the first Protocol to the European Convention on Human Rights obliges all signatory parties to guarantee the right to education. At world level, the United Nations’ International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights of 1966 guarantees this right under its Article 13.
Educational systems are established to provide education and training, often for children and the young. A curriculum defines what students should know, understand and be able to do as the result of education. A teaching profession delivers teaching which enables learning, and a system of policies, regulations, examinations, structures and funding enables teachers to teach to the best of their abilities.
Primary (or elementary) education consists of the first
years of formal, structured education. In general, primary education consists of six or seven years of schooling starting at the age of 5 or 6, although this varies
between, and sometimes within, countries. Globally,
around 70% of primary-age children are enrolled in
primary education, and this proportion is rising.
In most contemporary educational systems of the world, secondary education consists of the second years of formal education that occur during adolescence. It is characterized by transition from the typically compulsory, comprehensive primary education for minors, to the optional, selective tertiary, “post-secondary”, or “higher” education (e.g., university, vocational school) for adults.
Higher education, also called tertiary, third stage, or
post secondary education, is the non-compulsory
educational level that follows the completion of a
school providing a secondary education, such as a
high school or secondary school. Tertiary education is
normally taken to include undergraduate and postgraduate education, as well as vocational education and
training. Colleges and universities are the main institutions that provide tertiary education. Collectively,
these are sometimes known as tertiary institutions.
Tertiary education generally results in the receipt of
certificates, diplomas, or academic degrees.
Education
Education encompasses both the teaching and learning of knowledge, proper conduct, and technical competency. It thus focuses on the cultivation of skills, trades or professions, as well as mental, moral & aesthetic development.
Formal education consists of systematic instruction, teaching and training by professional teachers. This consists of the application of pedagogy and the development of curricula.
The right to education is a fundamental human right. Since 1952, Article 2 of the first Protocol to the European Convention on Human Rights obliges all signatory parties to guarantee the right to education. At world level, the United Nations’ International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights of 1966 guarantees this right under its Article 13.
Educational systems are established to provide education and training, often for children and the young. A curriculum defines what students should know, understand and be able to do as the result of education. A teaching profession delivers teaching which enables learning, and a system of policies, regulations, examinations, structures and funding enables teachers to teach to the best of their abilities.
Primary (or elementary) education consists of the first
years of formal, structured education. In general, primary education consists of six or seven years of schooling starting at the age of 5 or 6, although this varies
between, and sometimes within, countries. Globally,
around 70% of primary-age children are enrolled in
primary education, and this proportion is rising.
In most contemporary educational systems of the world, secondary education consists of the second years of formal education that occur during adolescence. It is characterized by transition from the typically compulsory, comprehensive primary education for minors, to the optional, selective tertiary, “post-secondary”, or “higher” education (e.g., university, vocational school) for adults.
Higher education, also called tertiary, third stage, or
post secondary education, is the non-compulsory
educational level that follows the completion of a
school providing a secondary education, such as a
high school or secondary school. Tertiary education is
normally taken to include undergraduate and postgraduate education, as well as vocational education and
training. Colleges and universities are the main institutions that provide tertiary education. Collectively,
these are sometimes known as tertiary institutions.
Tertiary education generally results in the receipt of
certificates, diplomas, or academic degrees.
Education
Education encompasses both the teaching and learning of knowledge, proper conduct, and technical competency. It thus focuses on the cultivation of skills, trades or professions, as well as mental, moral & aesthetic development.
Formal education consists of systematic instruction, teaching and training by professional teachers. This consists of the application of pedagogy and the development of curricula.
The right to education is a fundamental human right. Since 1952, Article 2 of the first Protocol to the European Convention on Human Rights obliges all signatory parties to guarantee the right to education. At world level, the United Nations’ International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights of 1966 guarantees this right under its Article 13.
Educational systems are established to provide education and training, often for children and the young. A curriculum defines what students should know, understand and be able to do as the result of education. A teaching profession delivers teaching which enables learning, and a system of policies, regulations, examinations, structures and funding enables teachers to teach to the best of their abilities.
Primary (or elementary) education consists of the first
years of formal, structured education. In general, primary education consists of six or seven years of schooling starting at the age of 5 or 6, although this varies
between, and sometimes within, countries. Globally,
around 70% of primary-age children are enrolled in
primary education, and this proportion is rising.
In most contemporary educational systems of the world, secondary education consists of the second years of formal education that occur during adolescence. It is characterized by transition from the typically compulsory, comprehensive primary education for minors, to the optional, selective tertiary, “post-secondary”, or “higher” education (e.g., university, vocational school) for adults.
Higher education, also called tertiary, third stage, or
post secondary education, is the non-compulsory
educational level that follows the completion of a
school providing a secondary education, such as a
high school or secondary school. Tertiary education is
normally taken to include undergraduate and postgraduate education, as well as vocational education and
training. Colleges and universities are the main institutions that provide tertiary education. Collectively,
these are sometimes known as tertiary institutions.
Tertiary education generally results in the receipt of
certificates, diplomas, or academic degrees.
