Questões de Inglês - Tradução | Translation para Concurso
Foram encontradas 544 questões



CAUTION
PROPERHANDLINGOFTHE FINECARTRIDGES
Handle the FINE Cartridges of this product properly, observing
the cautions noted below. Improper handling causes
malfunction or other problems in the product, as well as
damage to the FINE Cartridges.
Note:
1) When you install the FINE cartridges in the product, insert
the FINE Cartridges into the FINE Cartridge Holder
carefully not to knock them against the sides of the holder.
Also be sure to install them in a well-lit environment.
For details, refer to your setup sheet.
2) Do not attempt to disassemble or modify the FINE
cartridges.
3) Do not handle the FINE Cartridges roughly such as
applying them excessive pressure or dropping them.
4) Do not rinse or wipe the FINE Cartridges.
5) Once you have installed the FINE Cartridges, do not
remove them unnecessarily.
(Taken from Canon Inc. 2008 - Printed in Vietnam)

For your protection, please read these safety
instructions completely before operating the appliance, and
keep this manual for future reference.
Carefully observe all warnings, precautions and
instructions on the appliance, or the one described in the
operating instructions and adhere to them.
POWER SOURCES - This set should be operated
only from the type of power source indicated on the marking
label. If you are not sure of the type of electrical power supplied
to your home, consult your dealer or local power company. For
those sets designed to operate from battery power, or other
sources, refer to the operating instructions.
OBJECTAND LIQUID ENTRY - Never push objects
of any kind into the set through openings as they may touch
dangerous voltage points or short out parts that could result in
a fire or electric shock. Never spill liquid of any kind on the set.
ATTACHMENTS - Do not use attachments not
recommended by the manufacturer, as they may cause
hazards.
CLEANING - Unplug the set from the wall outlet
before cleaning or polishing it. Do not use liquid cleaners or
aerosol cleaners. Use a cloth lightly dampened with water for
cleaning the exterior of the set.
OVERLOADING - Do not overload wall outlets,
extension cords or convenience receptacles beyond their
capacity, since this can result in fire or electric shock.
ACCESSORIES - Do not place the set on an
unstable cart, stand, tripod, bracket, or table. The set may
fall, causing serious injury to a child or an adult, and serious
damage to the set. Use only a cart stand tripod, bracket, or
table recommended by the manufacturer.
WATER AND MOISTURE - Do not use power-line
operated sets near water - for example, near a bathtub,
washbowl, kitchen sink, or laundry tub, in a wet basement, or
near a swimming pool, etc.
SERVICING - Do not attempt to service the set
yourself as opening or removing covers may expose you to
dangerous voltage or other hazards. Refer all servicing to
qualified service personnel.
SAFETY CHECK - Upon completion of any service
or repairs to the set, as the service technician to perform
routine safety checks (as specified by the manufacturer) to
determine that the set is in safe operating condition.
(Adapted from SONY manual - Sony Corporation - 2000 - Printed in Japan).
Posted on Friday March 27th, 2009 by Jebediah Reed
To give some sense of the pace of public works
construction in China, the city of Guangzhou is planning to open
83 miles of new subway lines by the end of next year.
Meanwhile, New York ? a city of about the same size ? has
been playing around with the 1.7-mile Second Avenue line for
decades now. China also builds subways rather cheaply ? $100
million per mile versus $ 2.4 billion per mile in the Big Apple.
Not surprisingly, projects there are more aggressive in all
respects: there are 60 tunnel boring machines operating in
Guangzhou, while only one is slated for the Second Avenue
project; workers put in five 12-hour shifts a week (and if they
don't like it, they can go pound glacial till); and seizing property
is a breeze.
An article in the Business section of today's NY Times
(Clash of Subways and Car Culture in Chinese Cities by Keith
Bradsher) [VERB] a smart look at the forces at play as China
goes on a transit infrastructure spending spree while it
simultaneously becomes evermore sprawling and car-centric.
Here's one interesting passage, [CONJUNCTION] the
story is worth reading in its entirety:
Western mass transit experts applaud China for investing
billions in systems that will put less stress on the environment
and on cities. But they warn that other Chinese policies, like
allowing real estate developers to build sprawling new suburbs,
undermine the benefits of the mass transit boom.
Mr. Chan Shao Zhang , a 67-year-old engineer in charge
of the works in Guangzhou, defended Guangzhou's combination
of cars and subways, saying that the city built a subway line to a new Toyota assembly plant to help employees and suppliers
reach it.
Subways have been most competitive in cities like New
York that have high prices for parking, and tolls for bridges and
tunnels, discouraging car use. Few Chinese cities have been
willing to follow suit, other than Shanghai, which charges a fee of
several thousand dollars for each license plate.
The cost and physical limitations of subways have
discouraged most cities from building new ones. For instance,
only Tokyo has a subway system that carries more people than
its buses. The buses are cheaper and able to serve far more
streets but move more slowly, pollute more and contribute to
traffic congestion.
China has reason to worry. It surpassed the United
States in total vehicle sales for the first time in January, although
the United States remained slightly ahead in car sales. But in
February, China overtook the United States in both, in part
because the global downturn has hurt auto sales much more in
the United States than in China.
There are many countervaling forces ..X.. China has
passed its own stimulus package and the government is eager
to put people to work, create economic activity, and build
modern infrastructure. The Guangzhou project is part of major
national transit buildout. But the nation's cities are also sprawling
beasts, and in that sense, more suited to cars than trains. Not
shockingly, many Chinese prefer the former.
(Adapted from http://www.infrastructurist.com/2009/03/27/-
building-a-subway-is-96-percent-cheaper-in-china/)
January 26, 2009
By John C. Dvorak
It's no coincidence that the computer industry peaked around the year 2000, went into a serious decline, stabilized at the low point a couple of years ago, and has since collapsed again.
A confluence of reasons is responsible for this, but when it comes to the industry bringing this on itself, one major event may have taken down the entire business.
I'm speaking about the announcement of the Itanium processor. This continues to be one of the great fiascos of the last 50 years, and not because Intel blew too much money on its development or that the chip performed poorly and will never be widely adopted. It was the reaction and subsequent consolidation in the industry that took place once this grandiose chip was preannounced.
We heard that HP, IBM, Dell, and even Sun Microsystems would use these chips and discontinue anything else they were developing. This included Sun making noise about dropping the SPARC chip for this thing - sight unseen. I say "sight unseen" because it would be years before the chip was even prototyped. The entire industry just took Intel at its word that Itanium would work as advertised in a PowerPoint presentation.
Because this chip was supposed to radically change the way computers work and become the driving force behind all systems in the future, one promising project after another was dropped. Why? Because Itanium was the future for all computing. Why bother wasting money on good ideas that didn't include it?
The failure of this chip to do anything more than exist as a niche processor sealed the fate of Intel - and perhaps the entire industry, since from 1997 to 2001 everyone waited for the messiah of chips to take us all to the next level.
It did that all right. It took us to the next level. But we didn't know that the next level was below us, not above.
(Adapted from PCMAG.COM)
Worm Infects Millions of Computers Worldwide
By JOHN MARKOFF
A new digital plague has hit the Internet, infecting millions of personal and usiness computers in what seems to be the first step of a multistage attack. The world's eading computer security experts do not yet know who programmed the infection, or what the next stage will be.
In recent weeks a worm, a malicious software program, has swept through corporate, educational and public computer networks around the world. Known as Conficker or Downandup, it is spread by a recently discovered Microsoft Windows vulnerability, by guessing network passwords and by hand-carried consumer gadgets like USB keys.
Experts say it is the
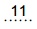 infection since the Slammer worm exploded through the Internet in January 2003, and it may have infected as many as nine million personal computers around the world.
infection since the Slammer worm exploded through the Internet in January 2003, and it may have infected as many as nine million personal computers around the world.Worms like Conficker not only ricochet around the Internet at lightning speed, they harness infected computers into unified systems called botnets, which can then accept programming instructions from their clandestine masters.
Many computer users may not notice that their machines have been infected, and computer security researchers said they were waiting for the instructions to materialize, to determine what impact the botnet will have on PC users. It might operate in the background, using the infected computer to send spam or infect other computers, or it might steal the PC user's personal information.
Microsoft rushed an emergency patch to defend the Windows operating systems against this vulnerability in October, yet the worm has continued to spread even as the level of warnings has grown in recent weeks.
Earlier this week, security researchers at Qualys, a Silicon Valley security firm, estimated that about 30 percent of Windows-based computers attached to the Internet remain vulnerable to infection because they have not been updated with the patch, despite the fact that it was made available in October.
Unraveling the program has been particularly challenging because it comes with encryption mechanisms that hide its internal workings from those seeking to disable it.
The program uses an elaborate shell-game-style technique to permit someone to command it remotely. Each day it generates a new list of 250 domain names. Instructions from any one of these domain names would be obeyed. To control the botnet, an attacker would need only to register a single domain to send instructions to the botnet globally, greatly complicating the task of law enforcement and security companies trying to intervene and block the activation of the botnet.
Several computer security firms said that although Conficker appeared to have been written from scratch, it had parallels to the work of a suspected Eastern European criminal gang that has profited by sending programs known as "scareware" to personal computers that seem to warn users of an infection and ask for credit card numbers to pay for bogus antivirus software that actually further infects their computer.
One intriguing clue left by the malware authors is that the first version of the program checked to see if the computer had a Ukrainian keyboard layout. If it found it had such a keyboard, it would not infect the machine, according to Phillip Porras, a security investigator at SRI International who has disassembled the program to determine how it functioned.
(Adapted from The New York Times)
Worm Infects Millions of Computers Worldwide
By JOHN MARKOFF
A new digital plague has hit the Internet, infecting millions of personal and usiness computers in what seems to be the first step of a multistage attack. The world's eading computer security experts do not yet know who programmed the infection, or what the next stage will be.
In recent weeks a worm, a malicious software program, has swept through corporate, educational and public computer networks around the world. Known as Conficker or Downandup, it is spread by a recently discovered Microsoft Windows vulnerability, by guessing network passwords and by hand-carried consumer gadgets like USB keys.
Experts say it is the
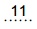 infection since the Slammer worm exploded through the Internet in January 2003, and it may have infected as many as nine million personal computers around the world.
infection since the Slammer worm exploded through the Internet in January 2003, and it may have infected as many as nine million personal computers around the world.Worms like Conficker not only ricochet around the Internet at lightning speed, they harness infected computers into unified systems called botnets, which can then accept programming instructions from their clandestine masters.
Many computer users may not notice that their machines have been infected, and computer security researchers said they were waiting for the instructions to materialize, to determine what impact the botnet will have on PC users. It might operate in the background, using the infected computer to send spam or infect other computers, or it might steal the PC user's personal information.
Microsoft rushed an emergency patch to defend the Windows operating systems against this vulnerability in October, yet the worm has continued to spread even as the level of warnings has grown in recent weeks.
Earlier this week, security researchers at Qualys, a Silicon Valley security firm, estimated that about 30 percent of Windows-based computers attached to the Internet remain vulnerable to infection because they have not been updated with the patch, despite the fact that it was made available in October.
Unraveling the program has been particularly challenging because it comes with encryption mechanisms that hide its internal workings from those seeking to disable it.
The program uses an elaborate shell-game-style technique to permit someone to command it remotely. Each day it generates a new list of 250 domain names. Instructions from any one of these domain names would be obeyed. To control the botnet, an attacker would need only to register a single domain to send instructions to the botnet globally, greatly complicating the task of law enforcement and security companies trying to intervene and block the activation of the botnet.
Several computer security firms said that although Conficker appeared to have been written from scratch, it had parallels to the work of a suspected Eastern European criminal gang that has profited by sending programs known as "scareware" to personal computers that seem to warn users of an infection and ask for credit card numbers to pay for bogus antivirus software that actually further infects their computer.
One intriguing clue left by the malware authors is that the first version of the program checked to see if the computer had a Ukrainian keyboard layout. If it found it had such a keyboard, it would not infect the machine, according to Phillip Porras, a security investigator at SRI International who has disassembled the program to determine how it functioned.
(Adapted from The New York Times)
Worm Infects Millions of Computers Worldwide
By JOHN MARKOFF
A new digital plague has hit the Internet, infecting millions of personal and usiness computers in what seems to be the first step of a multistage attack. The world's eading computer security experts do not yet know who programmed the infection, or what the next stage will be.
In recent weeks a worm, a malicious software program, has swept through corporate, educational and public computer networks around the world. Known as Conficker or Downandup, it is spread by a recently discovered Microsoft Windows vulnerability, by guessing network passwords and by hand-carried consumer gadgets like USB keys.
Experts say it is the
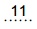 infection since the Slammer worm exploded through the Internet in January 2003, and it may have infected as many as nine million personal computers around the world.
infection since the Slammer worm exploded through the Internet in January 2003, and it may have infected as many as nine million personal computers around the world.Worms like Conficker not only ricochet around the Internet at lightning speed, they harness infected computers into unified systems called botnets, which can then accept programming instructions from their clandestine masters.
Many computer users may not notice that their machines have been infected, and computer security researchers said they were waiting for the instructions to materialize, to determine what impact the botnet will have on PC users. It might operate in the background, using the infected computer to send spam or infect other computers, or it might steal the PC user's personal information.
Microsoft rushed an emergency patch to defend the Windows operating systems against this vulnerability in October, yet the worm has continued to spread even as the level of warnings has grown in recent weeks.
Earlier this week, security researchers at Qualys, a Silicon Valley security firm, estimated that about 30 percent of Windows-based computers attached to the Internet remain vulnerable to infection because they have not been updated with the patch, despite the fact that it was made available in October.
Unraveling the program has been particularly challenging because it comes with encryption mechanisms that hide its internal workings from those seeking to disable it.
The program uses an elaborate shell-game-style technique to permit someone to command it remotely. Each day it generates a new list of 250 domain names. Instructions from any one of these domain names would be obeyed. To control the botnet, an attacker would need only to register a single domain to send instructions to the botnet globally, greatly complicating the task of law enforcement and security companies trying to intervene and block the activation of the botnet.
Several computer security firms said that although Conficker appeared to have been written from scratch, it had parallels to the work of a suspected Eastern European criminal gang that has profited by sending programs known as "scareware" to personal computers that seem to warn users of an infection and ask for credit card numbers to pay for bogus antivirus software that actually further infects their computer.
One intriguing clue left by the malware authors is that the first version of the program checked to see if the computer had a Ukrainian keyboard layout. If it found it had such a keyboard, it would not infect the machine, according to Phillip Porras, a security investigator at SRI International who has disassembled the program to determine how it functioned.
(Adapted from The New York Times)
Worm Infects Millions of Computers Worldwide
By JOHN MARKOFF
A new digital plague has hit the Internet, infecting millions of personal and usiness computers in what seems to be the first step of a multistage attack. The world's eading computer security experts do not yet know who programmed the infection, or what the next stage will be.
In recent weeks a worm, a malicious software program, has swept through corporate, educational and public computer networks around the world. Known as Conficker or Downandup, it is spread by a recently discovered Microsoft Windows vulnerability, by guessing network passwords and by hand-carried consumer gadgets like USB keys.
Experts say it is the
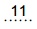 infection since the Slammer worm exploded through the Internet in January 2003, and it may have infected as many as nine million personal computers around the world.
infection since the Slammer worm exploded through the Internet in January 2003, and it may have infected as many as nine million personal computers around the world.Worms like Conficker not only ricochet around the Internet at lightning speed, they harness infected computers into unified systems called botnets, which can then accept programming instructions from their clandestine masters.
Many computer users may not notice that their machines have been infected, and computer security researchers said they were waiting for the instructions to materialize, to determine what impact the botnet will have on PC users. It might operate in the background, using the infected computer to send spam or infect other computers, or it might steal the PC user's personal information.
Microsoft rushed an emergency patch to defend the Windows operating systems against this vulnerability in October, yet the worm has continued to spread even as the level of warnings has grown in recent weeks.
Earlier this week, security researchers at Qualys, a Silicon Valley security firm, estimated that about 30 percent of Windows-based computers attached to the Internet remain vulnerable to infection because they have not been updated with the patch, despite the fact that it was made available in October.
Unraveling the program has been particularly challenging because it comes with encryption mechanisms that hide its internal workings from those seeking to disable it.
The program uses an elaborate shell-game-style technique to permit someone to command it remotely. Each day it generates a new list of 250 domain names. Instructions from any one of these domain names would be obeyed. To control the botnet, an attacker would need only to register a single domain to send instructions to the botnet globally, greatly complicating the task of law enforcement and security companies trying to intervene and block the activation of the botnet.
Several computer security firms said that although Conficker appeared to have been written from scratch, it had parallels to the work of a suspected Eastern European criminal gang that has profited by sending programs known as "scareware" to personal computers that seem to warn users of an infection and ask for credit card numbers to pay for bogus antivirus software that actually further infects their computer.
One intriguing clue left by the malware authors is that the first version of the program checked to see if the computer had a Ukrainian keyboard layout. If it found it had such a keyboard, it would not infect the machine, according to Phillip Porras, a security investigator at SRI International who has disassembled the program to determine how it functioned.
(Adapted from The New York Times)
Windows 7 gets the basics right. Here's what you need to know
about the new OS.
Harry McCracken, PC World
Monday, October 19, 2009 2:00 pm
What if a new version of Windows didn't try to dazzle
you? What if, instead, it tried to disappear except when you
needed it? Such an operating system would dispense with glitzy
effects in favor of low-key, useful new features. Rather than
pelting you with alerts, warnings, and requests, it would try to
stay out of your face. And if any bundled applications weren't
essential, it would dump 'em.
It's not a what-if scenario. Windows 7, set to arrive on
new PCs and as a shrinkwrapped upgrade on October 22, has a
minimalist feel and attempts to fix annoyances old and new. In
contrast, Windows Vista offered a flashy new interface, but its
poor performance, compatibility gotchas, and lack of compelling
features made some folks regret upgrading and others refuse to
leave Windows XP.
Windows 7 is hardly flawless. Some features feel
unfinished; others won't realize their potential without heavy
lifting by third parties. And some long-standing annoyances
remain intact. But overall, the final shipping version I test-drove
appears to be the worthy successor to Windows XP that Vista
never was.
(Adapted from
http://www.pcworld.com/article/172602/windows_7_review.html
Windows 7 gets the basics right. Here's what you need to know
about the new OS.
Harry McCracken, PC World
Monday, October 19, 2009 2:00 pm
What if a new version of Windows didn't try to dazzle
you? What if, instead, it tried to disappear except when you
needed it? Such an operating system would dispense with glitzy
effects in favor of low-key, useful new features. Rather than
pelting you with alerts, warnings, and requests, it would try to
stay out of your face. And if any bundled applications weren't
essential, it would dump 'em.
It's not a what-if scenario. Windows 7, set to arrive on
new PCs and as a shrinkwrapped upgrade on October 22, has a
minimalist feel and attempts to fix annoyances old and new. In
contrast, Windows Vista offered a flashy new interface, but its
poor performance, compatibility gotchas, and lack of compelling
features made some folks regret upgrading and others refuse to
leave Windows XP.
Windows 7 is hardly flawless. Some features feel
unfinished; others won't realize their potential without heavy
lifting by third parties. And some long-standing annoyances
remain intact. But overall, the final shipping version I test-drove
appears to be the worthy successor to Windows XP that Vista
never was.
(Adapted from
http://www.pcworld.com/article/172602/windows_7_review.html
to 40:
Unhappy families
Source: www.economist.co.uk
July 1st, 2004 (Adapted)
The story of Elián González, a small, shipwrecked
Cuban boy who was the center of an international
custody battle in 2000, should have taught that splitting
families makes for bad politics. Apparently, it seems not
to have done.
With his eye on holding Florida in this year's
presidential election, George Bush has tightened the
rules on contacts between Cuban-Americans and their
families back on the island. From June 30th, Cuban-
Americans can make only one two-week visit every
three years, instead of unrestricted annual visits. They
will not be able to send as much money to people on
the island, and none beyond their immediate families.
All humanitarian visits have been scrapped.
Analyze the following alternatives in order to find
the appropriate translation for their underlined
pieces into Portuguese:
to 40:
Unhappy families
Source: www.economist.co.uk
July 1st, 2004 (Adapted)
The story of Elián González, a small, shipwrecked
Cuban boy who was the center of an international
custody battle in 2000, should have taught that splitting
families makes for bad politics. Apparently, it seems not
to have done.
With his eye on holding Florida in this year's
presidential election, George Bush has tightened the
rules on contacts between Cuban-Americans and their
families back on the island. From June 30th, Cuban-
Americans can make only one two-week visit every
three years, instead of unrestricted annual visits. They
will not be able to send as much money to people on
the island, and none beyond their immediate families.
All humanitarian visits have been scrapped.
Analyze the following alternatives in order to find
the appropriate translation for their underlined
pieces into Portuguese:
to 40:
Unhappy families
Source: www.economist.co.uk
July 1st, 2004 (Adapted)
The story of Elián González, a small, shipwrecked
Cuban boy who was the center of an international
custody battle in 2000, should have taught that splitting
families makes for bad politics. Apparently, it seems not
to have done.
With his eye on holding Florida in this year's
presidential election, George Bush has tightened the
rules on contacts between Cuban-Americans and their
families back on the island. From June 30th, Cuban-
Americans can make only one two-week visit every
three years, instead of unrestricted annual visits. They
will not be able to send as much money to people on
the island, and none beyond their immediate families.
All humanitarian visits have been scrapped.
Analyze the following alternatives in order to find
the appropriate translation for their underlined
pieces into Portuguese:
and 22:
Brazil's foreign policy: A giant stirs
Source: www.economist.co.uk
June 10, 2004 (Adapted)
It is a small force, but of huge symbolic significance.
This month, 1,200 Brazilian troops arrived in Haiti, the
country's biggest foreign military deployment since the
second world war. Brazil is commanding a United
Nations peacekeeping force of 6,700 mainly Latin
American troops and 1,600 police which is taking over
from American and French forces in the Caribbean
island. This marks a new departure. Brazil has long
been a gentle and introverted giant, content to be a
bystander on the world stage. Now that is changing.
Analyze the alternatives below in order to choose
the appropriate translation for the two sentences
below into Portuguese:


