Questões de Concurso
Sobre aspectos linguísticos | linguistic aspects em inglês
Foram encontradas 850 questões
What are the major historical influences that contributed to the formation of the English language as we know it today, and how did they impact its vocabulary and grammar?
In the context of language as discourse, when considering the essential elements for effective communication within a specific situation, which of the following factors should be taken into consideration in ensuring successful interaction?
( A ) INFLECTION ( B ) DERIVATION
( ) refers to the formation of new lexemes – words. ( ) refers to the grammatical contrasts and distinctions. ( ) a stem is considered to be a semantic core of a word. ( ) a root is considered to be a semantic core of a word.
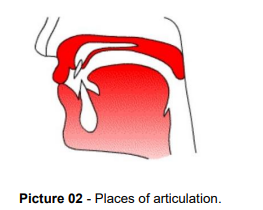
Not all stressed syllables are of equal importance. Some stressed syllables have greater prominence than others, and form the nucleus, or focal point, of an intonation pattern. We may describe a nucleus as a strongly stressed syllable which marks a major change of pitch direction, i.e. where the pitch goes up or down.
LEECH, G.; SVARTVIK, J., 2012, p. 36.
So, it is very important
Digital technology is everywhere, and it is changing the way citizens behave. From working patterns to the day-to-day services we use and the places we live, there is no aspect of modern life that remains untouched by digital tools and solutions. This represents both the biggest challenge and opportunity for public sector organizations as they seek to engage citizens and create future-proofed, sustainably-minded societies.
The public sector plays a key role in setting the sustainability agenda for society, including the approach to circularity and recycling. While private sector companies can greatly influence the successful achievement of sustainability targets, the public sector bears the responsibility for outlining how society can achieve these goals more broadly at both national and local levels. By embracing the same digital technologies that are transforming their citizens’ lives, public sector organizations can help pivot society towards a more sustainable tomorrow.
In addition, there has been a rise of smart cities and the circular economy. Urban areas account for 75% of global carbon dioxide emissions, and the 100 cities with the greatest footprints account for 18% of global emissions. But there are more than 70 cities worldwide pledging to become carbon neutral by 2050.
Public sector actors can fuel sustainable transformation by releasing capital to invest in sustainable city transformation projects and smart cities. By tapping into the value of data and green infrastructure, smart cities can combat climate risks and become more resilient to the many unexpected events of today’s increasingly unpredictable world. These cities can support the decoupling of resource use and environmental impacts by diffusing circular economy approaches to production and consumption.
Internet:<pulse.microsoft.com>
Based on the ideas presented in the previous text, as well as on its linguistic aspects, judge the following item.
The segment “more than”, in the last sentence of the third
paragraph, can be correctly replaced with over than without
changing the meaning of the text.
Digital technology is everywhere, and it is changing the way citizens behave. From working patterns to the day-to-day services we use and the places we live, there is no aspect of modern life that remains untouched by digital tools and solutions. This represents both the biggest challenge and opportunity for public sector organizations as they seek to engage citizens and create future-proofed, sustainably-minded societies.
The public sector plays a key role in setting the sustainability agenda for society, including the approach to circularity and recycling. While private sector companies can greatly influence the successful achievement of sustainability targets, the public sector bears the responsibility for outlining how society can achieve these goals more broadly at both national and local levels. By embracing the same digital technologies that are transforming their citizens’ lives, public sector organizations can help pivot society towards a more sustainable tomorrow.
In addition, there has been a rise of smart cities and the circular economy. Urban areas account for 75% of global carbon dioxide emissions, and the 100 cities with the greatest footprints account for 18% of global emissions. But there are more than 70 cities worldwide pledging to become carbon neutral by 2050.
Public sector actors can fuel sustainable transformation by releasing capital to invest in sustainable city transformation projects and smart cities. By tapping into the value of data and green infrastructure, smart cities can combat climate risks and become more resilient to the many unexpected events of today’s increasingly unpredictable world. These cities can support the decoupling of resource use and environmental impacts by diffusing circular economy approaches to production and consumption.
Internet:<pulse.microsoft.com>
Based on the ideas presented in the previous text, as well as on its linguistic aspects, judge the following item.
The text suggests that, although public sector organizations
have a minor role in setting the sustainability agenda for
society, they have great impact on the successful
achievement of sustainability goals.
Crazy Horse
Crazy Horse (Tasunke Witko, 1840-1877) was an Oglala Lakota Sioux warrior and warband leader considered among the greatest defenders of Sioux lands against the forces of the US government in the 19th century. He is one of the most famous Native American figures in history and among the Sioux's most honored heroes. Although he is often referred to as a "chief", Crazy Horse was actually a "Shirt Wearer" – a kind of "subchief" – who carried out the decisions of the council and also served as a war chief of a given band of warriors. Even so, Crazy Horse inspired such devotion in his followers that he was regarded as a "chief" and is referenced as such by others.
His name, Tasunke Witko (Crazy Horse), is accurately translated as "His Crazy Horse" or "His Horse is Crazy" and was his father's and grandfather's name, seemingly referencing a horse that behaved erratically. According to Black Elk, however, the name correlated to Crazy Horse's famous vision in which he saw his horse dancing as though "made only of shadow" in a strange or "crazy" way.
Crazy Horse dedicated himself to opposing the US military as early as 1854 following the Grattan Fight (Grattan Massacre) and the subsequent massacre of Little Thunder's camp in 1855 by Colonel William S. Harney. He continued his resistance over the next eleven years and was named a "Shirt Wearer" in 1865. He fought in the Battle of Plate River Bridge (1865), Red Cloud's War (1866-1868), the Battle of the Rosebud (1876), and the Battle of the Little Bighorn (1876). His last full-scale engagement with US forces was the Battle of Wolf Mountain in January 1877.
World History Encyclopedia. Adaptation.
Text CG1A2-II
The enormity of the global climate crisis is so vast that individual actions may seem meaningless: can installing LED lighting in my home or keeping my car tires inflated really help save the polar bears?
First coined by Portland, Oregon-based writer Emma Pattee, the climate shadow aims to paint a picture of the full sum of one’s choices — and the impact they have on the planet.
In an article she wrote in 2021, Pattee detailed her concept for measuring an individual’s impact: “Your climate shadow is a dark shape stretching out behind you. Everywhere you go, it goes too, tallying not just your air conditioning use and the gas mileage of your car, but also how you vote, how many children you choose to have, where you work, how you invest your money, how much you talk about climate change, and whether your words amplify urgency, apathy, or denial.” The larger the shadow — the greater an individual’s impact on doing good for the planet.
In other words, rather than incentivizing purely individual actions, your climate shadow grows when those actions inspire others, knowingly or otherwise.
Kieran Mulvaney. Climate shadow is what really matters.
National Geographic (adapted).
Action 1: Teacher has students repeat pronunciation of specific words in a text. Action 2: Teacher asks students about their favorite sports after reading a text on rugby. Action 3: Teacher uses a well-known short story to present the simple past. Action 4: Teacher plays the corresponding audio to a text presented in class.
I have 12 years old. - I goed to school yesterday. - I am with a headache. - She work in the morning.
Corrected – worked – seemed – studied
Sheep –ship – Cheap – Chip
The vowel sounds present in the words below correspond to the minimal pair:
Heat – hit