Questões de Concurso
Comentadas para profissional de meio ambiente júnior
Foram encontradas 80 questões
Resolva questões gratuitamente!
Junte-se a mais de 4 milhões de concurseiros!
A norma ABNT NBR ISO 31.010/2012 define as principais técnicas para o processo de avaliação de riscos como parte do sistema de gestão. Existe uma técnica que inicialmente busca identificar os riscos mais significativos e os menos significativos, com o objetivo de assegurar que os recursos para controle serão focados nos riscos mais significativos. Há ainda o cuidado de não deixar de fora os riscos que ocorrem com frequência, mas têm um efeito cumulativo importante.
O método descrito acima é denominado
Segundo a NBR 10.004/2004, um resíduo é classificado como perigoso ou não, por suas características. Essa norma estabelece, ainda, códigos para identificação dos resíduos.
Um resíduo que possui a característica de ser uma substância que pode liberar oxigênio e, como resultado, estimular a combustão e aumentar a intensidade do fogo em outro material, é classificado como perigoso devido à
De acordo com o Decreto n° 4.339/2002, em relação ao componente Conservação da Biodiversidade, uma diretriz está relacionada à conservação ex situ de espécies.
Um dos objetivos específicos consiste em desenvolver, promover e apoiar estudos e estabelecer metodologias para conservação e manutenção dos bancos das espécies nativas e exóticas de interesses científico e comercial relativos à(ao)
De acordo com a Lei n° 9.985/2000, existe o grupo das Unidades de Proteção Integral, entre as quais aquela que tem como objetivo a preservação da natureza e a realização de pesquisas científicas.
Trata-se da Unidade denominada
De acordo com o Decreto n° 8.127/2013, fica instituído o Plano Nacional de Contingência para Incidentes de Poluição por Óleo em Águas sob Jurisdição Nacional (PNC).
O documento técnico que contém, de forma detalhada, procedimentos operacionais, recursos humanos e materiais necessários à execução das ações de resposta, em incidente de poluição por óleo de significância nacional, é denominado
Nos termos do Decreto n° 5.098/2004, fica criado o Plano Nacional de Prevenção, Preparação e Resposta Rápida a Emergências Ambientais com Produtos Químicos Perigosos – (P2R2), com o objetivo de prevenir a ocorrência de acidentes com produtos químicos perigosos e aprimorar o sistema de preparação e resposta a emergências químicas no País.
Um dos princípios orientadores da P2R2 é a
As populações tradicionais, cujo estilo de vida é baseado em atividades de pesca, na faixa litorânea do sudeste e sul do Brasil, compostas principalmente por mestiços de indígenas e colonizadores europeus, são denominadas
Nesse sentido, qual é a destinação adequada do óleo lubrificante usado ou contaminado, conforme determinam as Resoluções Conama nº 9, de 31/08/1993, e Conama nº 362, de 23/06/2005?
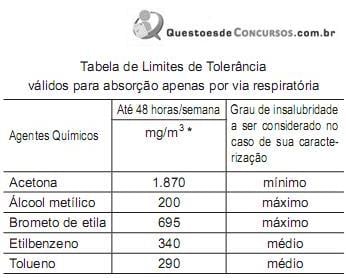
* mg/m³ - miligramas por metro cúbico de ar
Uma avaliação dos agentes químicos de uma indústria apresentou o seguinte resultado para a média aritmética das concentrações:
• Acetona = 2.130 mg/m³
• Álcool metílico = 105 mg/m³
• Brometo de etila = 715 mg/m³
• Etilbenzeno = 365 mg/m³
• Tolueno = 302 mg/m³
Portanto, no ambiente de trabalho dessa indústria, para jornada de trabalho de até 48 horas por semana, tomando por base as considerações e os dados acima, o agente químico que apresenta a condição e o grau de insalubridade é este:
O marciano encontrou-me na rua e teve medo de minha impossibilidade humana. Como pode existir, pensou consigo, um ser que no existir põe tamanha anulação de existência?
Afastou-se o marciano, e persegui-o. Precisava dele como de um testemunho. Mas, recusando o colóquio, desintegrou-se no ar constelado de problemas.
E fiquei só em mim, de mim ausente.
ANDRADE, Carlos Drummond de. Science fiction. Poesia e prosa. Rio de Janeiro: Nova Aguilar, 1988, p. 330-331.
A frase abaixo deverá sofrer algumas alterações nas palavras em destaque para adequar-se à norma-padrão.
A muito tempo não vejo a parte da minha família a qual foi deixada de herança a fazenda a que todos devotavam grande afeto.
De acordo com a norma-padrão, a correção implicaria, respectivamente, esta sequência de palavras:
Some of you may be familiar with OSHA - the Occupational Safety & Health Administration. The sole purpose of this agency is to keep American workers safe. Complying with OSHA regulations isn't always easy, but if we work together, we can do it. Yet, complying with regulations is not the real reason for working safely. Our real motive is simple. We care about each and every one of you and will do what is necessary to prevent you from being injured.
However, keeping our workplace safe takes input from everyone. Management, supervisor, and all of you have to come together on this issue, or we're in trouble. For example, upper management has to approve the purchase of safe equipment. Supervisors, including myself, have to ensure that each of you knows how to use that equipment safely. Then it's up to you to follow through the task and use the equipment as you were trained. If any one part of this chain fails, accidents are going to happen and people are going to get hurt.
Responsibility Number One - Recognize Hazards
At the core of your safety responsibilities lies the task of recognizing safety and health hazards. In order to do that, you must first understand what constitutes a hazard. Extreme hazards are often obvious. Our hopes are that you won't find too many of those around here.
There are, however, more subtle hazards that won't jump up and bite you. As a result of your safety training and meetings like these, some things may come to mind. For example, a machine may not be easy to lock out. Common practice may be to use a tag. This is a potential hazard and should be discussed. Maybe something can be changed to make it easier to use a lock. Other subtle hazards include such things as frayed electrical cords, a loose machine guard, a cluttered aisle, or maybe something that just doesn't look right.
Responsibility Number Two - Report Hazards
A big part of recognizing hazards is using your instincts. Nobody knows your job as well as you do, so we're counting on you to let us know about possible problems. Beyond recognizing hazards, you have to correct them or report them to someone who can. This too, is a judgement call. For example, if something spills in your work area you can probably clean it up yourself. However, if there is an unlabeled chemical container and you have no idea what it is, you should report it to your supervisor.
Additional Employee Responsibilities
Good housekeeping is a major part of keeping your work area safe. For example, you should take a few minutes each day to ensure that aisles, hallways, and stairways in your work area are not obstructed. If boxes, equipment, or anything else is left to pile up, you have a tripping hazard on your hands. Those obstructions could keep you from exiting the building quickly and safely should you face an emergency situation.
Also watch out for spills. These can lead to slips and falls. Flammable materials are another thing to be aware of. Make sure they are disposed of properly.
Keep Thinking. Even if you're doing your job safely and you are avoiding hazards, there are often even better ways to work safely. If you have ideas for improving the safety of your job or that of co-workers, share them.
Concluding Remarks
While nothing we do can completely eliminate the threat of an incident, we can work together to improve our odds. As I said, this must be a real team effort and I'm counting on input from all of you. Let's keep communicating and continue to improve safety.
Available at: <http://www.ncsu.edu/ehs/www99/right/training/meeting/emplores.html>.Retrieved on: April 1st, 2012. Adapted.
Some of you may be familiar with OSHA - the Occupational Safety & Health Administration. The sole purpose of this agency is to keep American workers safe. Complying with OSHA regulations isn't always easy, but if we work together, we can do it. Yet, complying with regulations is not the real reason for working safely. Our real motive is simple. We care about each and every one of you and will do what is necessary to prevent you from being injured.
However, keeping our workplace safe takes input from everyone. Management, supervisor, and all of you have to come together on this issue, or we're in trouble. For example, upper management has to approve the purchase of safe equipment. Supervisors, including myself, have to ensure that each of you knows how to use that equipment safely. Then it's up to you to follow through the task and use the equipment as you were trained. If any one part of this chain fails, accidents are going to happen and people are going to get hurt.
Responsibility Number One - Recognize Hazards
At the core of your safety responsibilities lies the task of recognizing safety and health hazards. In order to do that, you must first understand what constitutes a hazard. Extreme hazards are often obvious. Our hopes are that you won't find too many of those around here.
There are, however, more subtle hazards that won't jump up and bite you. As a result of your safety training and meetings like these, some things may come to mind. For example, a machine may not be easy to lock out. Common practice may be to use a tag. This is a potential hazard and should be discussed. Maybe something can be changed to make it easier to use a lock. Other subtle hazards include such things as frayed electrical cords, a loose machine guard, a cluttered aisle, or maybe something that just doesn't look right.
Responsibility Number Two - Report Hazards
A big part of recognizing hazards is using your instincts. Nobody knows your job as well as you do, so we're counting on you to let us know about possible problems. Beyond recognizing hazards, you have to correct them or report them to someone who can. This too, is a judgement call. For example, if something spills in your work area you can probably clean it up yourself. However, if there is an unlabeled chemical container and you have no idea what it is, you should report it to your supervisor.
Additional Employee Responsibilities
Good housekeeping is a major part of keeping your work area safe. For example, you should take a few minutes each day to ensure that aisles, hallways, and stairways in your work area are not obstructed. If boxes, equipment, or anything else is left to pile up, you have a tripping hazard on your hands. Those obstructions could keep you from exiting the building quickly and safely should you face an emergency situation.
Also watch out for spills. These can lead to slips and falls. Flammable materials are another thing to be aware of. Make sure they are disposed of properly.
Keep Thinking. Even if you're doing your job safely and you are avoiding hazards, there are often even better ways to work safely. If you have ideas for improving the safety of your job or that of co-workers, share them.
Concluding Remarks
While nothing we do can completely eliminate the threat of an incident, we can work together to improve our odds. As I said, this must be a real team effort and I'm counting on input from all of you. Let's keep communicating and continue to improve safety.
Available at: <http://www.ncsu.edu/ehs/www99/right/training/meeting/emplores.html>.Retrieved on: April 1st, 2012. Adapted.
Some of you may be familiar with OSHA - the Occupational Safety & Health Administration. The sole purpose of this agency is to keep American workers safe. Complying with OSHA regulations isn't always easy, but if we work together, we can do it. Yet, complying with regulations is not the real reason for working safely. Our real motive is simple. We care about each and every one of you and will do what is necessary to prevent you from being injured.
However, keeping our workplace safe takes input from everyone. Management, supervisor, and all of you have to come together on this issue, or we're in trouble. For example, upper management has to approve the purchase of safe equipment. Supervisors, including myself, have to ensure that each of you knows how to use that equipment safely. Then it's up to you to follow through the task and use the equipment as you were trained. If any one part of this chain fails, accidents are going to happen and people are going to get hurt.
Responsibility Number One - Recognize Hazards
At the core of your safety responsibilities lies the task of recognizing safety and health hazards. In order to do that, you must first understand what constitutes a hazard. Extreme hazards are often obvious. Our hopes are that you won't find too many of those around here.
There are, however, more subtle hazards that won't jump up and bite you. As a result of your safety training and meetings like these, some things may come to mind. For example, a machine may not be easy to lock out. Common practice may be to use a tag. This is a potential hazard and should be discussed. Maybe something can be changed to make it easier to use a lock. Other subtle hazards include such things as frayed electrical cords, a loose machine guard, a cluttered aisle, or maybe something that just doesn't look right.
Responsibility Number Two - Report Hazards
A big part of recognizing hazards is using your instincts. Nobody knows your job as well as you do, so we're counting on you to let us know about possible problems. Beyond recognizing hazards, you have to correct them or report them to someone who can. This too, is a judgement call. For example, if something spills in your work area you can probably clean it up yourself. However, if there is an unlabeled chemical container and you have no idea what it is, you should report it to your supervisor.
Additional Employee Responsibilities
Good housekeeping is a major part of keeping your work area safe. For example, you should take a few minutes each day to ensure that aisles, hallways, and stairways in your work area are not obstructed. If boxes, equipment, or anything else is left to pile up, you have a tripping hazard on your hands. Those obstructions could keep you from exiting the building quickly and safely should you face an emergency situation.
Also watch out for spills. These can lead to slips and falls. Flammable materials are another thing to be aware of. Make sure they are disposed of properly.
Keep Thinking. Even if you're doing your job safely and you are avoiding hazards, there are often even better ways to work safely. If you have ideas for improving the safety of your job or that of co-workers, share them.
Concluding Remarks
While nothing we do can completely eliminate the threat of an incident, we can work together to improve our odds. As I said, this must be a real team effort and I'm counting on input from all of you. Let's keep communicating and continue to improve safety.
Available at: <http://www.ncsu.edu/ehs/www99/right/training/meeting/emplores.html>.Retrieved on: April 1st, 2012. Adapted.