Questões Militares
Para exército
Foram encontradas 23.643 questões
Resolva questões gratuitamente!
Junte-se a mais de 4 milhões de concurseiros!
A conduta adequada é:
Nessa paciente, a conduta correta é descontinuar o uso de
A causa mais provável da hipercalemia desse paciente é:
Nesse momento, o manejo mais adequado é:
Em que parte(s) do sistema nervoso localizam-se os sintomas dessa paciente?
O diagnóstico mais provável é infecção por
Nesse momento, o tratamento farmacológico mais adequado é:
Nesse momento, o medicamento que deve ser prescrito é:
Para esse paciente, a conduta correta é:
Nesse momento, a conduta inicial correta é solicitar
A deficiência de qual micronutriente é a etiologia mais provável dos sintomas dessa paciente?
O diagnóstico mais provável é:
Nesse momento, a conduta correta é:
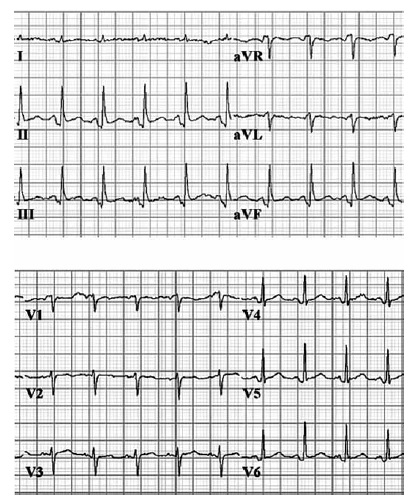
Nesse paciente, a conduta correta é:
A próxima conduta recomendada é:
Nessa paciente, o exame mais apropriado a ser solicitado é
Nesse momento, a conduta recomendada é:
A conduta inicial correta é prescrever