Questões de Concurso
Para trt - 16ª região (ma)
Foram encontradas 2.081 questões
Resolva questões gratuitamente!
Junte-se a mais de 4 milhões de concurseiros!
Se Z tem distribuição normal padrão, então:
P(Z < 0,25) = 0,599, P(Z < 0,80) = 0,84, P(Z < 1) = 0,841, P(Z < 1,96) = 0,975, P(Z < 3,09) = 0,999
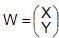 uma variável aleatória com distribuição normal multivariada com vetor de médias
uma variável aleatória com distribuição normal multivariada com vetor de médias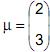 e matriz de covariâncias
e matriz de covariâncias 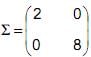 . Seja a variável aleatória U = 2X - Y. A probabilidade de U assumir um valor entre 2 e 5, denotada por P(2 < U < 5) é igual a
. Seja a variável aleatória U = 2X - Y. A probabilidade de U assumir um valor entre 2 e 5, denotada por P(2 < U < 5) é igual a Se Z tem distribuição normal padrão, então:
P(Z < 0,25) = 0,599, P(Z < 0,80) = 0,84, P(Z < 1) = 0,841, P(Z < 1,96) = 0,975, P(Z < 3,09) = 0,999
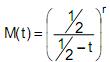 , para t < ½ e onde r é parâmetro de X.
, para t < ½ e onde r é parâmetro de X. O valor de r para que X tenha distribuição qui-quadrado com 12 graus de liberdade é dado por
Se e é a base dos logaritmos naturais, tem-se
e-1 = 0,37, e-1,2 = 0,30, e-1,5 = 0,22, e-2 = 0,14.
Se e é a base dos logaritmos naturais, tem-se
e-1 = 0,37, e-1,2 = 0,30, e-1,5 = 0,22, e-2 = 0,14.

Nessas condições, a esperança condicional de Y dado x, denotada por
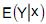 é igual a
é igual a I. A análise de correspondência permite estudar associação entre variáveis qualitativas.
II. Na análise discriminante a variável dependente deve ser métrica.
III. Na análise de regressão múltipla uma forma de identificar colinearidade entre as variáveis independentes é examinar as correlações entre essas variáveis.
IV. Na análise de conglomerados, as técnicas hierárquicas exigem que o usuário identifique previamente o número de grupos desejado, mas essa exigência não prevalece nas técnicas não hierárquicas.
Está correto o que se afirma APENAS em
 , considere:
, considere:I. A região de admissibilidade do modelo é
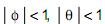 .
. II. Sua função de autocorrelação, dada por f(k), k = 1,2, ... decai exponencialmente após k = 1.
III. Sua função de autocorrelação parcial, dada por g(k), k = 1,2,..., só é diferente de zero para k = 1.
IV. Se
 = 0,
= 0, 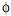 = 0,5 e a média do modelo é 2, a previsão de origem t e horizonte 1 é igual a 1.
= 0,5 e a média do modelo é 2, a previsão de origem t e horizonte 1 é igual a 1. Está correto o que se afirma APENAS em


 2) é igual a
2) é igual a  + ßt +
+ ßt +  , t = 1, 2, 3 ... para prever o volume de vendas (Yt ), em milhões de reais, no ano (2002 + t). Os parâmetros
, t = 1, 2, 3 ... para prever o volume de vendas (Yt ), em milhões de reais, no ano (2002 + t). Os parâmetros  e ß são desconhecidos e et corresponde ao erro aleatório com as respectivas hipóteses do modelo de regressão linear simples. Com base nas informações de 2003 até 2012 e utilizando o método dos mínimos quadrados obteve-se as estimativas de
e ß são desconhecidos e et corresponde ao erro aleatório com as respectivas hipóteses do modelo de regressão linear simples. Com base nas informações de 2003 até 2012 e utilizando o método dos mínimos quadrados obteve-se as estimativas de e ß. Observação:
e ß. Observação:  e
e  correspondem às médias de t e Y no período considerado e seus valores são 5,5 e 20, respectivamente.
correspondem às médias de t e Y no período considerado e seus valores são 5,5 e 20, respectivamente. 
 0 (hipótese alternativa), obtém-se que o correspondente valor da estatística t (t calculado), para ser comparado com o respectivo t tabelado, pertence ao intervalo
0 (hipótese alternativa), obtém-se que o correspondente valor da estatística t (t calculado), para ser comparado com o respectivo t tabelado, pertence ao intervalo  + ßt +
+ ßt +  , t = 1, 2, 3 ... para prever o volume de vendas (Yt ), em milhões de reais, no ano (2002 + t). Os parâmetros
, t = 1, 2, 3 ... para prever o volume de vendas (Yt ), em milhões de reais, no ano (2002 + t). Os parâmetros  e ß são desconhecidos e et corresponde ao erro aleatório com as respectivas hipóteses do modelo de regressão linear simples. Com base nas informações de 2003 até 2012 e utilizando o método dos mínimos quadrados obteve-se as estimativas de
e ß são desconhecidos e et corresponde ao erro aleatório com as respectivas hipóteses do modelo de regressão linear simples. Com base nas informações de 2003 até 2012 e utilizando o método dos mínimos quadrados obteve-se as estimativas de e ß. Observação:
e ß. Observação:  e
e  correspondem às médias de t e Y no período considerado e seus valores são 5,5 e 20, respectivamente.
correspondem às médias de t e Y no período considerado e seus valores são 5,5 e 20, respectivamente. 
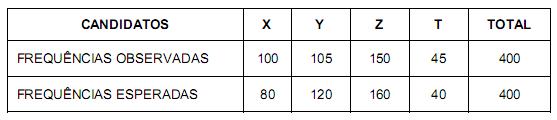
Deseja-se testar com base nesta tabela, utilizando o teste qui-quadrado, as seguintes hipóteses:
H0: não há discrepância entre as frequências observadas e esperadas (hipótese nula).
H1: as frequências observadas e esperadas são discrepantes (hipótese alternativa).
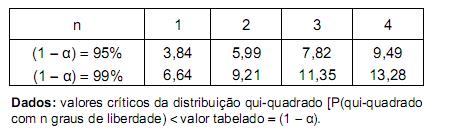
Uma conclusão correta é que
 50% (hipótese alternativa). Com a aproximação da distribuição binomial pela normal, sem a correção de continuidade, foi apurado o valor do escore reduzido r correspondente para comparação com o valor crítico z da distribuição normal padrão Z tal que a probabilidade
50% (hipótese alternativa). Com a aproximação da distribuição binomial pela normal, sem a correção de continuidade, foi apurado o valor do escore reduzido r correspondente para comparação com o valor crítico z da distribuição normal padrão Z tal que a probabilidade 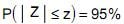 .Se r = 2,5, então x é igual a
.Se r = 2,5, então x é igual a